readme.md
In kcf-jackson/ADtools: Automatic Differentiation Toolbox
R package ‘ADtools’
Implements the forward-mode auto-differentiation for multivariate
functions using the matrix-calculus notation from Magnus and Neudecker
(1988). Two key features of the package are: (i) the package
incorporates various optimisaton strategies to improve performance; this
includes applying memoisation to cut down object construction time,
using sparse matrix representation to save derivative calculation, and
creating specialised matrix operations with Rcpp to reduce computation
time; (ii) the package supports differentiating random variable with
respect to their parameters, targetting MCMC (and in general
simulation-based) applications.
Installation
devtools::install_github("kcf-jackson/ADtools")
Notation
Given a function  , where
, where  , the Jacobina matrix
of
, the Jacobina matrix
of 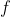 w.r.t.
w.r.t.
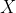 is given by
is given by

Example 1. Matrix multiplication
Function definition
Consider  where
where 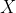 is a matrix, and
is a matrix, and 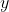 is a
vector.
is a
vector.
library(ADtools)
f <- function(X, y) X %*% y
X <- randn(2, 2)
y <- matrix(c(1, 1))
print(list(X = X, y = y, f = f(X, y)))
## $X
## [,1] [,2]
## [1,] 0.41331040 0.7085659
## [2,] 0.01066195 -1.2300747
##
## $y
## [,1]
## [1,] 1
## [2,] 1
##
## $f
## [,1]
## [1,] 1.121876
## [2,] -1.219413
Auto-differentiation
Since 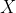 has dimension (2,
2) and
has dimension (2,
2) and 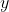 has dimension
(2, 1), the input space has dimension
has dimension
(2, 1), the input space has dimension  , and the output has dimension
, and the output has dimension
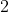 , i.e.
, i.e.
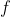 maps
maps
 to
to
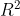 and the
Jacobian of
and the
Jacobian of 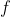 should be
should be
 .
.
# Full Jacobian matrix
f_AD <- auto_diff(f, at = list(X = X, y = y))
f_AD@dx # returns a Jacobian matrix
## d_X1 d_X2 d_X3 d_X4 d_y1 d_y2
## d_output_1 1 0 1 0 0.41331040 0.7085659
## d_output_2 0 1 0 1 0.01066195 -1.2300747
auto_diff also supports computing a partial Jacobian matrix. For
instance, suppose we are only interested in the derivative w.r.t. y,
then we can run
f_AD <- auto_diff(f, at = list(X = X, y = y), wrt = "y")
f_AD@dx # returns a partial Jacobian matrix
## d_y1 d_y2
## d_output_1 0.41331040 0.7085659
## d_output_2 0.01066195 -1.2300747
Finite-differencing
It is good practice to always check the result with finite-differencing.
This can be done by calling finite_diff which has the same interface
as auto_diff.
f_FD <- finite_diff(f, at = list(X = X, y = y))
f_FD
## d_X1 d_X2 d_X3 d_X4 d_y1 d_y2
## d_output_1 1 0 1 0 0.41331039 0.7085659
## d_output_2 0 1 0 1 0.01066194 -1.2300747
Example 2. Estimating a linear regression model
Simulate data from 
set.seed(123)
n <- 1000
p <- 3
X <- randn(n, p)
beta <- randn(p, 1)
y <- X %*% beta + rnorm(n)
Inference with gradient descent
gradient_descent <- function(f, vary, fix, learning_rate = 0.01, tol = 1e-6, show = F) {
repeat {
df <- auto_diff(f, at = append(vary, fix), wrt = names(vary))
if (show) print(df@x)
delta <- learning_rate * as.numeric(df@dx)
vary <- relist(unlist(vary) - delta, vary)
if (max(abs(delta)) < tol) break
}
vary
}
lm_loss <- function(y, X, beta) sum((y - X %*% beta)^2)
# Estimate
gradient_descent(
f = lm_loss, vary = list(beta = rnorm(p, 1)), fix = list(y = y, X = X), learning_rate = 1e-4
)
## $beta
## [1] -0.1417494 -0.3345771 -1.4484226
# Truth
t(beta)
## [,1] [,2] [,3]
## [1,] -0.1503075 -0.3277571 -1.448165
Example 3. Sensitivity analysis of MCMC algorithms
Simulate data from 
set.seed(123)
n <- 30 # small data
p <- 10
X <- randn(n, p)
beta <- randn(p, 1)
y <- X %*% beta + rnorm(n)
Estimating a Bayesian linear regression model

Inference using Gibbs sampler
gibbs_gaussian <- function(X, y, b_0, B_0, alpha_0, delta_0, num_steps = 1e4) {
# Initialisation
init_sigma <- 1 / sqrt(rgamma0(1, alpha_0 / 2, scale = 2 / delta_0))
n <- length(y)
alpha_1 <- alpha_0 + n
sigma_g <- init_sigma
inv_B_0 <- solve(B_0)
inv_B_0_times_b_0 <- inv_B_0 %*% b_0
XTX <- crossprod(X)
XTy <- crossprod(X, y)
beta_res <- vector("list", num_steps)
sigma_res <- vector("list", num_steps)
pb <- txtProgressBar(1, num_steps, style = 3)
for (i in 1:num_steps) {
# Update beta
B_g <- solve(sigma_g^(-2) * XTX + inv_B_0)
b_g <- B_g %*% (sigma_g^(-2) * XTy + inv_B_0_times_b_0)
beta_g <- t(rmvnorm0(1, b_g, B_g))
# Update sigma
delta_g <- delta_0 + sum((y - X %*% beta_g)^2)
sigma_g <- 1 / sqrt(rgamma0(1, alpha_1 / 2, scale = 2 / delta_g))
# Keep track
beta_res[[i]] <- beta_g
sigma_res[[i]] <- sigma_g
setTxtProgressBar(pb, i)
}
list(sigma = sigma_res, beta = beta_res)
}
Auto-differentiation
gibbs_deriv <- auto_diff(
gibbs_gaussian,
at = list(
b_0 = numeric(p), B_0 = diag(p), alpha_0 = 4, delta_0 = 4,
X = X, y = y, num_steps = 5000
),
wrt = c("b_0", "B_0", "alpha_0", "delta_0")
)
Computing the sensitivity of the posterior mean of 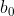 w.r.t. all the prior hyperparameters
w.r.t. all the prior hyperparameters
library(magrittr)
library(knitr)
library(kableExtra)
matrix_ls_to_array <- function(x) {
structure(unlist(x), dim = c(dim(x[[1]]), length(x)), dimnames = dimnames(x[[1]]))
}
tidy_mcmc <- function(mcmc_res, var0) {
mcmc_res[[var0]] %>%
purrr::map(~.x@dx) %>%
matrix_ls_to_array()
}
tidy_table <- function(x) {
x %>% kable() %>% kable_styling() %>% scroll_box(width = "100%")
}
posterior_Jacobian <- apply(tidy_mcmc(gibbs_deriv, "beta"), c(1,2), mean)
tidy_table(posterior_Jacobian)
d\_b\_01
d\_b\_02
d\_b\_03
d\_b\_04
d\_b\_05
d\_b\_06
d\_b\_07
d\_b\_08
d\_b\_09
d\_b\_010
d\_B\_01
d\_B\_02
d\_B\_03
d\_B\_04
d\_B\_05
d\_B\_06
d\_B\_07
d\_B\_08
d\_B\_09
d\_B\_010
d\_B\_011
d\_B\_012
d\_B\_013
d\_B\_014
d\_B\_015
d\_B\_016
d\_B\_017
d\_B\_018
d\_B\_019
d\_B\_020
d\_B\_021
d\_B\_022
d\_B\_023
d\_B\_024
d\_B\_025
d\_B\_026
d\_B\_027
d\_B\_028
d\_B\_029
d\_B\_030
d\_B\_031
d\_B\_032
d\_B\_033
d\_B\_034
d\_B\_035
d\_B\_036
d\_B\_037
d\_B\_038
d\_B\_039
d\_B\_040
d\_B\_041
d\_B\_042
d\_B\_043
d\_B\_044
d\_B\_045
d\_B\_046
d\_B\_047
d\_B\_048
d\_B\_049
d\_B\_050
d\_B\_051
d\_B\_052
d\_B\_053
d\_B\_054
d\_B\_055
d\_B\_056
d\_B\_057
d\_B\_058
d\_B\_059
d\_B\_060
d\_B\_061
d\_B\_062
d\_B\_063
d\_B\_064
d\_B\_065
d\_B\_066
d\_B\_067
d\_B\_068
d\_B\_069
d\_B\_070
d\_B\_071
d\_B\_072
d\_B\_073
d\_B\_074
d\_B\_075
d\_B\_076
d\_B\_077
d\_B\_078
d\_B\_079
d\_B\_080
d\_B\_081
d\_B\_082
d\_B\_083
d\_B\_084
d\_B\_085
d\_B\_086
d\_B\_087
d\_B\_088
d\_B\_089
d\_B\_090
d\_B\_091
d\_B\_092
d\_B\_093
d\_B\_094
d\_B\_095
d\_B\_096
d\_B\_097
d\_B\_098
d\_B\_099
d\_B\_0100
d\_alpha\_01
d\_delta\_01
d\_output\_1
0.0569887
0.0240169
\-0.0085018
\-0.0114905
\-0.0002056
\-0.0099043
0.0069673
\-0.0250403
\-0.0138359
0.0184303
\-0.0441342
\-0.0186824
0.0065791
0.0089195
0.0001676
0.0077123
\-0.0054299
0.0194540
0.0107661
\-0.0143304
\-0.0422326
\-0.0177185
0.0062827
0.0085277
0.0001388
0.0073738
\-0.0051957
0.0186088
0.0102891
\-0.0137093
\-0.0548737
\-0.0230575
0.0082968
0.0110663
0.0001859
0.0095235
\-0.0066902
0.0241129
0.0132928
\-0.0177620
\-0.0718000
\-0.0302760
0.0107191
0.0145789
0.0002573
0.0124716
\-0.0087673
0.0315428
0.0174258
\-0.0232140
\-0.0156627
\-0.0065633
0.0023708
0.0031359
0.0001308
0.0027179
\-0.0019058
0.0068750
0.0037912
\-0.0050542
0.0418913
0.0176076
\-0.0062615
\-0.0084694
\-0.0001351
\-0.0071959
0.0051419
\-0.0184411
\-0.0101835
0.0135673
\-0.1016804
\-0.0428326
0.0151174
0.0204964
0.0003181
0.0176513
\-0.0123461
0.0446991
0.0246896
\-0.0329021
0.0099753
0.0042146
\-0.0014552
\-0.0019818
\-0.0000670
\-0.0017475
0.0011945
\-0.0043029
\-0.0024432
0.0032439
0.0687012
0.0289268
\-0.0102440
\-0.0138316
\-0.0001937
\-0.0119421
0.0084227
\-0.0302179
\-0.0166070
0.0222462
0.1152496
0.0486374
\-0.0171780
\-0.0232862
\-0.0003697
\-0.0199968
0.0140737
\-0.0506390
\-0.0280183
0.0373722
\-0.0018965
0.0016811
d\_output\_2
0.0240377
0.0904281
0.0127987
\-0.0154678
0.0011496
\-0.0297209
0.0192483
\-0.0162636
\-0.0265724
0.0235886
\-0.0183982
\-0.0700067
\-0.0099287
0.0119620
\-0.0008713
0.0230590
\-0.0149584
0.0126714
0.0206031
\-0.0183164
\-0.0177858
\-0.0670336
\-0.0095958
0.0114911
\-0.0009177
0.0222430
\-0.0144052
0.0121760
0.0198080
\-0.0176238
\-0.0232262
\-0.0869873
\-0.0120353
0.0149244
\-0.0011250
0.0286433
\-0.0185164
0.0156581
0.0255766
\-0.0227551
\-0.0303404
\-0.1139404
\-0.0160980
0.0197683
\-0.0014266
0.0374066
\-0.0242106
0.0204458
0.0334838
\-0.0296973
\-0.0066046
\-0.0247385
\-0.0034116
0.0041890
\-0.0001068
0.0081420
\-0.0052474
0.0044657
0.0072442
\-0.0064331
0.0176188
0.0663741
0.0094205
\-0.0114027
0.0009022
\-0.0216447
0.0141864
\-0.0120085
\-0.0195519
0.0173548
\-0.0428613
\-0.1613073
\-0.0230086
0.0275584
\-0.0021971
0.0529932
\-0.0341142
0.0290588
0.0474033
\-0.0421258
0.0040008
0.0157923
0.0023707
\-0.0025788
0.0001263
\-0.0052141
0.0032759
\-0.0025446
\-0.0046489
0.0041278
0.0289120
0.1089914
0.0154794
\-0.0185779
0.0015487
\-0.0358662
0.0232800
\-0.0196546
\-0.0318409
0.0285183
0.0487821
0.1830006
0.0259046
\-0.0314158
0.0024403
\-0.0600001
0.0388629
\-0.0329070
\-0.0538610
0.0480035
\-0.0051331
0.0045483
d\_output\_3
\-0.0085091
0.0128582
0.0606947
0.0018708
0.0093748
\-0.0038372
\-0.0124373
0.0108905
\-0.0013585
0.0035816
0.0066996
\-0.0100238
\-0.0470345
\-0.0014486
\-0.0072611
0.0030017
0.0096190
\-0.0084236
0.0010817
\-0.0028071
0.0064625
\-0.0094615
\-0.0454735
\-0.0014125
\-0.0070568
0.0028694
0.0093231
\-0.0081605
0.0009901
\-0.0026940
0.0081889
\-0.0123584
\-0.0585021
\-0.0017899
\-0.0090490
0.0037064
0.0120127
\-0.0105169
0.0013044
\-0.0034779
0.0106775
\-0.0162045
\-0.0763825
\-0.0022640
\-0.0117940
0.0048318
0.0156772
\-0.0137081
0.0017181
\-0.0045021
0.0023308
\-0.0035036
\-0.0166668
\-0.0005309
\-0.0025077
0.0010566
0.0034371
\-0.0029829
0.0003518
\-0.0009703
\-0.0063362
0.0093897
0.0447738
0.0013822
0.0069415
\-0.0027284
\-0.0091884
0.0080518
\-0.0009880
0.0026380
0.0152430
\-0.0228882
\-0.1084255
\-0.0033729
\-0.0168030
0.0068048
0.0223176
\-0.0194609
0.0023904
\-0.0063921
\-0.0015991
0.0022439
0.0107478
0.0003773
0.0016300
\-0.0006714
\-0.0022394
0.0020392
\-0.0002404
0.0006235
\-0.0103342
0.0154750
0.0733211
0.0022912
0.0113836
\-0.0046196
\-0.0150125
0.0131633
\-0.0015559
0.0043453
\-0.0171223
0.0260386
0.1225932
0.0037405
0.0189755
\-0.0077206
\-0.0251427
0.0219994
\-0.0027912
0.0073362
\-0.0016336
0.0014212
d\_output\_4
\-0.0115148
\-0.0155222
0.0018741
0.0538145
\-0.0020646
0.0030748
\-0.0087192
0.0141244
0.0141004
\-0.0121362
0.0090350
0.0119581
\-0.0015009
\-0.0416657
0.0016067
\-0.0023328
0.0067214
\-0.0109202
\-0.0108953
0.0093877
0.0087038
0.0117329
\-0.0014675
\-0.0402955
0.0015294
\-0.0022764
0.0065180
\-0.0105615
\-0.0105698
0.0090910
0.0111127
0.0150710
\-0.0017092
\-0.0520296
0.0019920
\-0.0029658
0.0084436
\-0.0136627
\-0.0136540
0.0117369
0.0144505
0.0195160
\-0.0023350
\-0.0675164
0.0026036
\-0.0038820
0.0109700
\-0.0177700
\-0.0177239
0.0152723
0.0031468
0.0042670
\-0.0004861
\-0.0148352
0.0006424
\-0.0008148
0.0024087
\-0.0038815
\-0.0038776
0.0033266
\-0.0085681
\-0.0115627
0.0013937
0.0396951
\-0.0015198
0.0023721
\-0.0064352
0.0104493
0.0104159
\-0.0090011
0.0206229
0.0278116
\-0.0034118
\-0.0961119
0.0036398
\-0.0055483
0.0156814
\-0.0252497
\-0.0252152
0.0216987
\-0.0021391
\-0.0027703
0.0003903
0.0095449
\-0.0003900
0.0005380
\-0.0015780
0.0026081
0.0025117
\-0.0021678
\-0.0139711
\-0.0188096
0.0022905
0.0650464
\-0.0024392
0.0037289
\-0.0105230
0.0170629
0.0171256
\-0.0146613
\-0.0232066
\-0.0313395
0.0037780
0.1086399
\-0.0041298
0.0062744
\-0.0176437
0.0285431
0.0284539
\-0.0244253
\-0.0016562
0.0014197
d\_output\_5
\-0.0002015
0.0011602
0.0093305
\-0.0021301
0.0416820
0.0063474
\-0.0124201
\-0.0084977
0.0127248
0.0140695
0.0000392
\-0.0009037
\-0.0072236
0.0016548
\-0.0322917
\-0.0049382
0.0096484
0.0065554
\-0.0098702
\-0.0108998
0.0000799
\-0.0010397
\-0.0070015
0.0015956
\-0.0311980
\-0.0047749
0.0093385
0.0063402
\-0.0095232
\-0.0105459
0.0002337
\-0.0011615
\-0.0091311
0.0019994
\-0.0403015
\-0.0061458
0.0119972
0.0082189
\-0.0123143
\-0.0135727
0.0002891
\-0.0014201
\-0.0117045
0.0025540
\-0.0522549
\-0.0079484
0.0155687
0.0106572
\-0.0159636
\-0.0176338
0.0000658
\-0.0003473
\-0.0025924
0.0005953
\-0.0115158
\-0.0017385
0.0033803
0.0023231
\-0.0034806
\-0.0038647
\-0.0000968
0.0009752
0.0069060
\-0.0015688
0.0307289
0.0045695
\-0.0091735
\-0.0062613
0.0093726
0.0104121
0.0003115
\-0.0021644
\-0.0166177
0.0038501
\-0.0743845
\-0.0112928
0.0220746
0.0151891
\-0.0226929
\-0.0251613
0.0000843
0.0002798
0.0016057
\-0.0004489
0.0073900
0.0011070
\-0.0021410
\-0.0016478
0.0022166
0.0025215
\-0.0001848
0.0014832
0.0112817
\-0.0026156
0.0503344
0.0076649
\-0.0150416
\-0.0102730
0.0152763
0.0170167
\-0.0004861
0.0022518
0.0188271
\-0.0042536
0.0841183
0.0127844
\-0.0250641
\-0.0171571
0.0257523
0.0282801
0.0021382
\-0.0018787
d\_output\_6
\-0.0098928
\-0.0297162
\-0.0037695
0.0030480
0.0063663
0.0552486
\-0.0143575
0.0052084
0.0107802
0.0029326
0.0074214
0.0230069
0.0029022
\-0.0022937
\-0.0049406
\-0.0428277
0.0111680
\-0.0040983
\-0.0083541
\-0.0022415
0.0072248
0.0217703
0.0027583
\-0.0020931
\-0.0046577
\-0.0413635
0.0107642
\-0.0039331
\-0.0079740
\-0.0022010
0.0096220
0.0285772
0.0033567
\-0.0029425
\-0.0061197
\-0.0534077
0.0138521
\-0.0050280
\-0.0103800
\-0.0028076
0.0124796
0.0373442
0.0047290
\-0.0041209
\-0.0080016
\-0.0692467
0.0179884
\-0.0065145
\-0.0135446
\-0.0036905
0.0027195
0.0080265
0.0009267
\-0.0007802
\-0.0019473
\-0.0150756
0.0038894
\-0.0014342
\-0.0029022
\-0.0008212
\-0.0071938
\-0.0216834
\-0.0027394
0.0022030
0.0046396
0.0405590
\-0.0106023
0.0038578
0.0079088
0.0022191
0.0175856
0.0529079
0.0068558
\-0.0053461
\-0.0112332
\-0.0985946
0.0253945
\-0.0093039
\-0.0191869
\-0.0052745
\-0.0015026
\-0.0050982
\-0.0007503
0.0003666
0.0011963
0.0097106
\-0.0024161
0.0006043
0.0018568
0.0005551
\-0.0118376
\-0.0357508
\-0.0045558
0.0035470
0.0075299
0.0667830
\-0.0173927
0.0063052
0.0127777
0.0035293
\-0.0201816
\-0.0602960
\-0.0076860
0.0063388
0.0127583
0.1115422
\-0.0289714
0.0105507
0.0219431
0.0056070
0.0048153
\-0.0042268
d\_output\_7
0.0069446
0.0192320
\-0.0124953
\-0.0086532
\-0.0124090
\-0.0143473
0.0558417
\-0.0146184
\-0.0051602
\-0.0035448
\-0.0051272
\-0.0148759
0.0097013
0.0066371
0.0096298
0.0111660
\-0.0432957
0.0113787
0.0040087
0.0027347
\-0.0050374
\-0.0139463
0.0094648
0.0063540
0.0092342
0.0107642
\-0.0418240
0.0109867
0.0038158
0.0026658
\-0.0067943
\-0.0184984
0.0123624
0.0084440
0.0120081
0.0139189
\-0.0540180
0.0141399
0.0049925
0.0034015
\-0.0087916
\-0.0242142
0.0156719
0.0111644
0.0156054
0.0179926
\-0.0700294
0.0183071
0.0065053
0.0044500
\-0.0019214
\-0.0051924
0.0035041
0.0023222
0.0036054
0.0039501
\-0.0152366
0.0040064
0.0013745
0.0009905
0.0050195
0.0139367
\-0.0093230
\-0.0063717
\-0.0091359
\-0.0103301
0.0413188
\-0.0108259
\-0.0037585
\-0.0026864
\-0.0123397
\-0.0342099
0.0222600
0.0153796
0.0220557
0.0255470
\-0.0996328
0.0261613
0.0091591
0.0063636
0.0009729
0.0032416
\-0.0021301
\-0.0013462
\-0.0022680
\-0.0025112
0.0097469
\-0.0022555
\-0.0008595
\-0.0006834
0.0082659
0.0230507
\-0.0151265
\-0.0103304
\-0.0148400
\-0.0173030
0.0675348
\-0.0176816
\-0.0059760
\-0.0042830
0.0142285
0.0391065
\-0.0251826
\-0.0176514
\-0.0249597
\-0.0289096
0.1127846
\-0.0295681
\-0.0105792
\-0.0068367
\-0.0050240
0.0044264
d\_output\_8
\-0.0250804
\-0.0161938
0.0109440
0.0141087
\-0.0084907
0.0051460
\-0.0146053
0.0673064
0.0047617
\-0.0103918
0.0193901
0.0123672
\-0.0085698
\-0.0107848
0.0066224
\-0.0038823
0.0111201
\-0.0522336
\-0.0036282
0.0080575
0.0187944
0.0119589
\-0.0082823
\-0.0105283
0.0064342
\-0.0038049
0.0108549
\-0.0505127
\-0.0035369
0.0078282
0.0242659
0.0156709
\-0.0106651
\-0.0137003
0.0081853
\-0.0050257
0.0142004
\-0.0650318
\-0.0046159
0.0100563
0.0314683
0.0204053
\-0.0137138
\-0.0178233
0.0105922
\-0.0065138
0.0184283
\-0.0843316
\-0.0060171
0.0130294
0.0068385
0.0043584
\-0.0030011
\-0.0038238
0.0022621
\-0.0013739
0.0038935
\-0.0183673
\-0.0012828
0.0028227
\-0.0185725
\-0.0119098
0.0081547
0.0104460
\-0.0063207
0.0037169
\-0.0108092
0.0498851
0.0035081
\-0.0076994
0.0449804
0.0289774
\-0.0196031
\-0.0252719
0.0153021
\-0.0091713
0.0260506
\-0.1207382
\-0.0085237
0.0186647
\-0.0042959
\-0.0026810
0.0019020
0.0023368
\-0.0014871
0.0008146
\-0.0023603
0.0116123
0.0007876
\-0.0018047
\-0.0303050
\-0.0194974
0.0132639
0.0170032
\-0.0103353
0.0061868
\-0.0176369
0.0814000
0.0056628
\-0.0125827
\-0.0507465
\-0.0328884
0.0220748
0.0286126
\-0.0171680
0.0104383
\-0.0296133
0.1359903
0.0097023
\-0.0211098
0.0015298
\-0.0013439
d\_output\_9
\-0.0138377
\-0.0266094
\-0.0013464
0.0141003
0.0127371
0.0108331
\-0.0052421
0.0048221
0.0530128
\-0.0142592
0.0106016
0.0204647
0.0009927
\-0.0108144
\-0.0098145
\-0.0083304
0.0039921
\-0.0038836
\-0.0410147
0.0110594
0.0103596
0.0196407
0.0009328
\-0.0104557
\-0.0094673
\-0.0080459
0.0037988
\-0.0038664
\-0.0396832
0.0107345
0.0134222
0.0256635
0.0011410
\-0.0136421
\-0.0123035
\-0.0104722
0.0050322
\-0.0046676
\-0.0512514
0.0138072
0.0173695
0.0334742
0.0017008
\-0.0178857
\-0.0160227
\-0.0136459
0.0066662
\-0.0059179
\-0.0664936
0.0178668
0.0037365
0.0072135
0.0003140
\-0.0037982
\-0.0036054
\-0.0029823
0.0015032
\-0.0012083
\-0.0144189
0.0038367
\-0.0102321
\-0.0195538
\-0.0009581
0.0104256
0.0093853
0.0078496
\-0.0038132
0.0036739
0.0392466
\-0.0105759
0.0247708
0.0475729
0.0024715
\-0.0252144
\-0.0227486
\-0.0193319
0.0092072
\-0.0086815
\-0.0949740
0.0255564
\-0.0021981
\-0.0043490
\-0.0002609
0.0022409
0.0021664
0.0017800
\-0.0007949
0.0006660
0.0088741
\-0.0023693
\-0.0167036
\-0.0320287
\-0.0016078
0.0169591
0.0152770
0.0130280
\-0.0062642
0.0059658
0.0639315
\-0.0172731
\-0.0280732
\-0.0539748
\-0.0027756
0.0286292
0.0256939
0.0218936
\-0.0106074
0.0097172
0.1072256
\-0.0290052
0.0027076
\-0.0023674
d\_output\_10
0.0183998
0.0235696
0.0035820
\-0.0121090
0.0140323
0.0028750
\-0.0034804
\-0.0103564
\-0.0142733
0.0604927
\-0.0145180
\-0.0181169
\-0.0026837
0.0092915
\-0.0108873
\-0.0023307
0.0028632
0.0081400
0.0110213
\-0.0467783
\-0.0140121
\-0.0179260
\-0.0025975
0.0089999
\-0.0105325
\-0.0022815
0.0028046
0.0079632
0.0107114
\-0.0453199
\-0.0177544
\-0.0229244
\-0.0036911
0.0116933
\-0.0135718
\-0.0027779
0.0033604
0.0100647
0.0138165
\-0.0584723
\-0.0229918
\-0.0295581
\-0.0045324
0.0150177
\-0.0176017
\-0.0035554
0.0042804
0.0129093
0.0178981
\-0.0758737
\-0.0050233
\-0.0064541
\-0.0010407
0.0033427
\-0.0040061
\-0.0008135
0.0009901
0.0029355
0.0039354
\-0.0164856
0.0137477
0.0177026
0.0026546
\-0.0089431
0.0103514
0.0019110
\-0.0025516
\-0.0076565
\-0.0106108
0.0448584
\-0.0330814
\-0.0424295
\-0.0063049
0.0217503
\-0.0250430
\-0.0050663
0.0060199
0.0185659
0.0256592
\-0.1084753
0.0033399
0.0040222
0.0004825
\-0.0021145
0.0024388
0.0005097
\-0.0005756
\-0.0020969
\-0.0024352
0.0102202
0.0223668
0.0286054
0.0042865
\-0.0146718
0.0168359
0.0034689
\-0.0042721
\-0.0125683
\-0.0174525
0.0730667
0.0369782
0.0475096
0.0072398
\-0.0244064
0.0282180
0.0056742
\-0.0068803
\-0.0207674
\-0.0287255
0.1219028
0.0038724
\-0.0033642
kcf-jackson/ADtools documentation built on Nov. 16, 2020, 7:12 p.m.
R package ‘ADtools’
Implements the forward-mode auto-differentiation for multivariate functions using the matrix-calculus notation from Magnus and Neudecker (1988). Two key features of the package are: (i) the package incorporates various optimisaton strategies to improve performance; this includes applying memoisation to cut down object construction time, using sparse matrix representation to save derivative calculation, and creating specialised matrix operations with Rcpp to reduce computation time; (ii) the package supports differentiating random variable with respect to their parameters, targetting MCMC (and in general simulation-based) applications.
Installation
devtools::install_github("kcf-jackson/ADtools")
Notation
Given a function , where
, the Jacobina matrix
of
w.r.t.
is given by
Example 1. Matrix multiplication
Function definition
Consider where
is a matrix, and
is a
vector.
library(ADtools)
f <- function(X, y) X %*% y
X <- randn(2, 2)
y <- matrix(c(1, 1))
print(list(X = X, y = y, f = f(X, y)))
## $X
## [,1] [,2]
## [1,] 0.41331040 0.7085659
## [2,] 0.01066195 -1.2300747
##
## $y
## [,1]
## [1,] 1
## [2,] 1
##
## $f
## [,1]
## [1,] 1.121876
## [2,] -1.219413
Auto-differentiation
Since has dimension (2,
2) and
has dimension
(2, 1), the input space has dimension
, and the output has dimension
, i.e.
maps
to
and the
Jacobian of
should be
.
# Full Jacobian matrix
f_AD <- auto_diff(f, at = list(X = X, y = y))
f_AD@dx # returns a Jacobian matrix
## d_X1 d_X2 d_X3 d_X4 d_y1 d_y2
## d_output_1 1 0 1 0 0.41331040 0.7085659
## d_output_2 0 1 0 1 0.01066195 -1.2300747
auto_diff also supports computing a partial Jacobian matrix. For
instance, suppose we are only interested in the derivative w.r.t. y,
then we can run
f_AD <- auto_diff(f, at = list(X = X, y = y), wrt = "y")
f_AD@dx # returns a partial Jacobian matrix
## d_y1 d_y2
## d_output_1 0.41331040 0.7085659
## d_output_2 0.01066195 -1.2300747
Finite-differencing
It is good practice to always check the result with finite-differencing.
This can be done by calling finite_diff which has the same interface
as auto_diff.
f_FD <- finite_diff(f, at = list(X = X, y = y))
f_FD
## d_X1 d_X2 d_X3 d_X4 d_y1 d_y2
## d_output_1 1 0 1 0 0.41331039 0.7085659
## d_output_2 0 1 0 1 0.01066194 -1.2300747
Example 2. Estimating a linear regression model
Simulate data from 
set.seed(123)
n <- 1000
p <- 3
X <- randn(n, p)
beta <- randn(p, 1)
y <- X %*% beta + rnorm(n)
Inference with gradient descent
gradient_descent <- function(f, vary, fix, learning_rate = 0.01, tol = 1e-6, show = F) {
repeat {
df <- auto_diff(f, at = append(vary, fix), wrt = names(vary))
if (show) print(df@x)
delta <- learning_rate * as.numeric(df@dx)
vary <- relist(unlist(vary) - delta, vary)
if (max(abs(delta)) < tol) break
}
vary
}
lm_loss <- function(y, X, beta) sum((y - X %*% beta)^2)
# Estimate
gradient_descent(
f = lm_loss, vary = list(beta = rnorm(p, 1)), fix = list(y = y, X = X), learning_rate = 1e-4
)
## $beta
## [1] -0.1417494 -0.3345771 -1.4484226
# Truth
t(beta)
## [,1] [,2] [,3]
## [1,] -0.1503075 -0.3277571 -1.448165
Example 3. Sensitivity analysis of MCMC algorithms
Simulate data from 
set.seed(123)
n <- 30 # small data
p <- 10
X <- randn(n, p)
beta <- randn(p, 1)
y <- X %*% beta + rnorm(n)
Estimating a Bayesian linear regression model
Inference using Gibbs sampler
gibbs_gaussian <- function(X, y, b_0, B_0, alpha_0, delta_0, num_steps = 1e4) {
# Initialisation
init_sigma <- 1 / sqrt(rgamma0(1, alpha_0 / 2, scale = 2 / delta_0))
n <- length(y)
alpha_1 <- alpha_0 + n
sigma_g <- init_sigma
inv_B_0 <- solve(B_0)
inv_B_0_times_b_0 <- inv_B_0 %*% b_0
XTX <- crossprod(X)
XTy <- crossprod(X, y)
beta_res <- vector("list", num_steps)
sigma_res <- vector("list", num_steps)
pb <- txtProgressBar(1, num_steps, style = 3)
for (i in 1:num_steps) {
# Update beta
B_g <- solve(sigma_g^(-2) * XTX + inv_B_0)
b_g <- B_g %*% (sigma_g^(-2) * XTy + inv_B_0_times_b_0)
beta_g <- t(rmvnorm0(1, b_g, B_g))
# Update sigma
delta_g <- delta_0 + sum((y - X %*% beta_g)^2)
sigma_g <- 1 / sqrt(rgamma0(1, alpha_1 / 2, scale = 2 / delta_g))
# Keep track
beta_res[[i]] <- beta_g
sigma_res[[i]] <- sigma_g
setTxtProgressBar(pb, i)
}
list(sigma = sigma_res, beta = beta_res)
}
Auto-differentiation
gibbs_deriv <- auto_diff(
gibbs_gaussian,
at = list(
b_0 = numeric(p), B_0 = diag(p), alpha_0 = 4, delta_0 = 4,
X = X, y = y, num_steps = 5000
),
wrt = c("b_0", "B_0", "alpha_0", "delta_0")
)
Computing the sensitivity of the posterior mean of 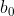 w.r.t. all the prior hyperparameters
w.r.t. all the prior hyperparameters
library(magrittr)
library(knitr)
library(kableExtra)
matrix_ls_to_array <- function(x) {
structure(unlist(x), dim = c(dim(x[[1]]), length(x)), dimnames = dimnames(x[[1]]))
}
tidy_mcmc <- function(mcmc_res, var0) {
mcmc_res[[var0]] %>%
purrr::map(~.x@dx) %>%
matrix_ls_to_array()
}
tidy_table <- function(x) {
x %>% kable() %>% kable_styling() %>% scroll_box(width = "100%")
}
posterior_Jacobian <- apply(tidy_mcmc(gibbs_deriv, "beta"), c(1,2), mean)
tidy_table(posterior_Jacobian)
Add the following code to your website.
For more information on customizing the embed code, read Embedding Snippets.
