README.md
In rrodrigojrr/ADW: A toolbox for spatial interpolation of meteorogical data
A toolbox for spatial interpolation by irregular meteorogical data observations (under development and review)
By: Rodrigo Lins Rocha Jr., Fabrício Daniel Santos Silva at Federal University of Alagoas
rodrigo.junior@icat.ufal.br,fabricio.santos@icat.ufal.br
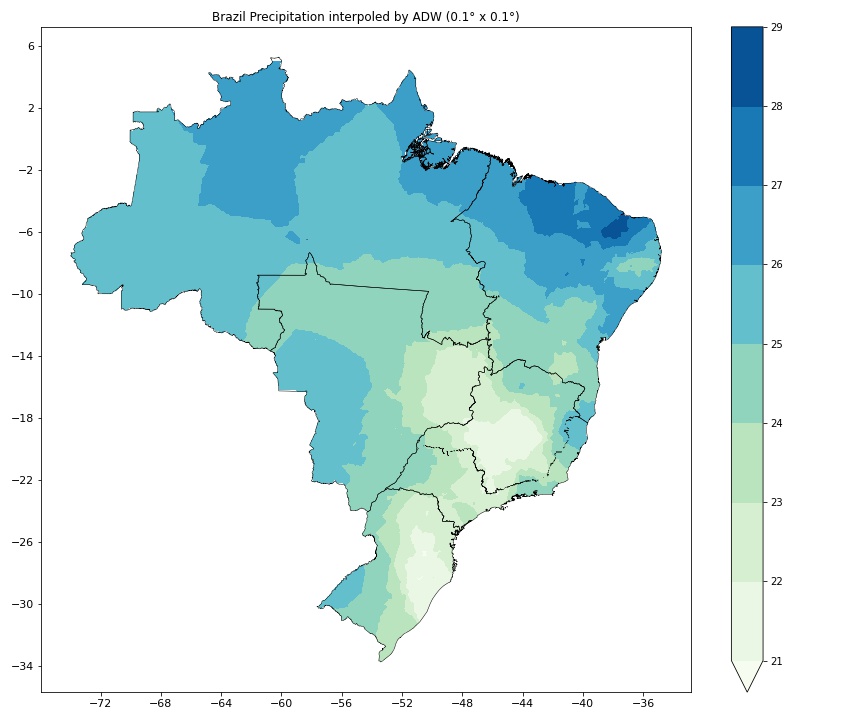
Introduction
Meteorologists several work with telemetric data by meteorological stations that measure fundamental variables. They usualy need some fields of this variables for make best analysis and forecast the atmosphere. This fields are obtained by spatial interpolation methods (SMP). Some methods used in most commun meteorogical softwares (GrADS and NCL) are actually smoth regular grid method, not being indicated for SPM. The concept of SPM is estimate a point with unknown observation using known observations in neighborhood meteorogical stations. The most efficient methods are based in Kringing or Inverse Distance Weighting (IDW). In operational aplicattions, Kringing is not indicated for hard automation fit a good variogram.
The IDW classical and variations are more indicated for meteorogical variables estimation because dispense manual fiting of models and preserves the original values of observations. Several works applied the IDW classical or variations for generate historical databases of meteorological variables (Xavier et al.,2016; Willmott and Matsuura, 2001; Hofstra, 2009). But, the weighting estimative of IDW is still slow for operational situations. For example: where is need make filds in high resoluton of temperature, precipitation, relative humidity, radiation and wind in 10 minuts interval.
This package has a set of tools for spatial interpolation by Sherpard methods (classical and variations) with functions that auxiliate the fast generation interpoled maps by witghts a priori estimed and saved. In this package there a function that apply a methodology for make a fast interpolation with weight apriori saved even if missing some observation, excluding tha necessity of new fiting. There also functions for validation of interpolation and export interpoled grid in netcdf output with or without spatial mask using shapefiles.
Instalation
Using the devtools package:
devtools::install_github("rrodrigojrr/ADW")
Using the remotes package:
remotes::install_github("rrodrigojrr/ADW")
Interpolation functions
Inverse distance weighting (IDW) is a type of deterministic method for multivariate interpolation with a known scattered set of points. The assigned values to unknown points are calculated with a weighted that variate in function of distance. The method did propose by Sherpard's (1968).
Radial Distance Weighting (RDW) is the first modifield version of Sherpard's algorithm where the estimative of weights consider the radius between the interpolation location x and the sample points xi.
Angular Distance Weighting (ADW) is the second modifield version of Sherpard's algorithm (Hofstra & New, 2009). The weights are estimed in function of the distance and angle between the sample stations. A parameter of this method is Correlation Distance Decay (CDD) that can change for each grid point. P.S: Actualy this method is constant forr all points in package ADW. This generate results very similiar to IDW classical. But is in development the automatition of calculation the CDD point by point. Using correlation of neighborhood stations this method produce fields more coherents with reality.
Export a netcdf output (With or without spatial mask)
Skill measure of interpoled method
A good interpolation depends of the best choose of parameters like power (p), radius (r) and Correlation Distance Decay (CDD). So, for test and choose the best method and parameters this package has the function skill that make a cross-validation in a data set. The function calcule the correlation, vies and compound relative error (CRE).
References:
HOFSTRA, Nynke; NEW, Mark. Spatial variability in correlation decay distance and influence on angular‐distance weighting interpolation of daily precipitation over Europe. International Journal of Climatology: A Journal of the Royal Meteorological Society, v. 29, n. 12, p. 1872-1880, 2009.
XAVIER, Alexandre C.; KING, Carey W.; SCANLON, Bridget R. Daily gridded meteorological variables in Brazil (1980–2013). International Journal of Climatology, v. 36, n. 6, p. 2644-2659, 2016.
SHEPARD, Donald. A two-dimensional interpolation function for irregularly-spaced data. In: Proceedings of the 1968 23rd ACM national conference. ACM, 1968. p. 517-524.
Willmott, C. J. and K. Matsuura (2001) Terrestrial Air Temperature and Precipitation: Monthly and Annual Time Series (1950 - 1999), http://climate.geog.udel.edu/~climate/html_pages/README.ghcn_ts2.html.
rrodrigojrr/ADW documentation built on Sept. 4, 2020, 8:12 a.m.
A toolbox for spatial interpolation by irregular meteorogical data observations (under development and review)
By: Rodrigo Lins Rocha Jr., Fabrício Daniel Santos Silva at Federal University of Alagoas rodrigo.junior@icat.ufal.br,fabricio.santos@icat.ufal.br

Introduction
Meteorologists several work with telemetric data by meteorological stations that measure fundamental variables. They usualy need some fields of this variables for make best analysis and forecast the atmosphere. This fields are obtained by spatial interpolation methods (SMP). Some methods used in most commun meteorogical softwares (GrADS and NCL) are actually smoth regular grid method, not being indicated for SPM. The concept of SPM is estimate a point with unknown observation using known observations in neighborhood meteorogical stations. The most efficient methods are based in Kringing or Inverse Distance Weighting (IDW). In operational aplicattions, Kringing is not indicated for hard automation fit a good variogram.
The IDW classical and variations are more indicated for meteorogical variables estimation because dispense manual fiting of models and preserves the original values of observations. Several works applied the IDW classical or variations for generate historical databases of meteorological variables (Xavier et al.,2016; Willmott and Matsuura, 2001; Hofstra, 2009). But, the weighting estimative of IDW is still slow for operational situations. For example: where is need make filds in high resoluton of temperature, precipitation, relative humidity, radiation and wind in 10 minuts interval.
This package has a set of tools for spatial interpolation by Sherpard methods (classical and variations) with functions that auxiliate the fast generation interpoled maps by witghts a priori estimed and saved. In this package there a function that apply a methodology for make a fast interpolation with weight apriori saved even if missing some observation, excluding tha necessity of new fiting. There also functions for validation of interpolation and export interpoled grid in netcdf output with or without spatial mask using shapefiles.
Instalation
Using the devtools package:
devtools::install_github("rrodrigojrr/ADW")
Using the remotes package:
remotes::install_github("rrodrigojrr/ADW")
Interpolation functions
Inverse distance weighting (IDW) is a type of deterministic method for multivariate interpolation with a known scattered set of points. The assigned values to unknown points are calculated with a weighted that variate in function of distance. The method did propose by Sherpard's (1968).
Radial Distance Weighting (RDW) is the first modifield version of Sherpard's algorithm where the estimative of weights consider the radius between the interpolation location x and the sample points xi.
Angular Distance Weighting (ADW) is the second modifield version of Sherpard's algorithm (Hofstra & New, 2009). The weights are estimed in function of the distance and angle between the sample stations. A parameter of this method is Correlation Distance Decay (CDD) that can change for each grid point. P.S: Actualy this method is constant forr all points in package ADW. This generate results very similiar to IDW classical. But is in development the automatition of calculation the CDD point by point. Using correlation of neighborhood stations this method produce fields more coherents with reality.
Export a netcdf output (With or without spatial mask)
Skill measure of interpoled method
A good interpolation depends of the best choose of parameters like power (p), radius (r) and Correlation Distance Decay (CDD). So, for test and choose the best method and parameters this package has the function skill that make a cross-validation in a data set. The function calcule the correlation, vies and compound relative error (CRE).
References:
HOFSTRA, Nynke; NEW, Mark. Spatial variability in correlation decay distance and influence on angular‐distance weighting interpolation of daily precipitation over Europe. International Journal of Climatology: A Journal of the Royal Meteorological Society, v. 29, n. 12, p. 1872-1880, 2009.
XAVIER, Alexandre C.; KING, Carey W.; SCANLON, Bridget R. Daily gridded meteorological variables in Brazil (1980–2013). International Journal of Climatology, v. 36, n. 6, p. 2644-2659, 2016.
SHEPARD, Donald. A two-dimensional interpolation function for irregularly-spaced data. In: Proceedings of the 1968 23rd ACM national conference. ACM, 1968. p. 517-524.
Willmott, C. J. and K. Matsuura (2001) Terrestrial Air Temperature and Precipitation: Monthly and Annual Time Series (1950 - 1999), http://climate.geog.udel.edu/~climate/html_pages/README.ghcn_ts2.html.
Add the following code to your website.
For more information on customizing the embed code, read Embedding Snippets.
