README.md
In tjtnew/reportfactory: Lightweight Infrastructure for Handling Multiple Rmarkdown Documents
Welcome to reportfactory!
NOTE
This version of {reportfactory} works in a very different way to the
previous unreleased version. For those already using {reportfactory} in
their pipelines you can obtain the old version using the {remotes}
package:
remotes::install_github("reconhub/reportfactory@old_version")
You can also download it directly from
https://github.com/reconhub/reportfactory/releases/tag/old_version.
reportfactory in a nutshell
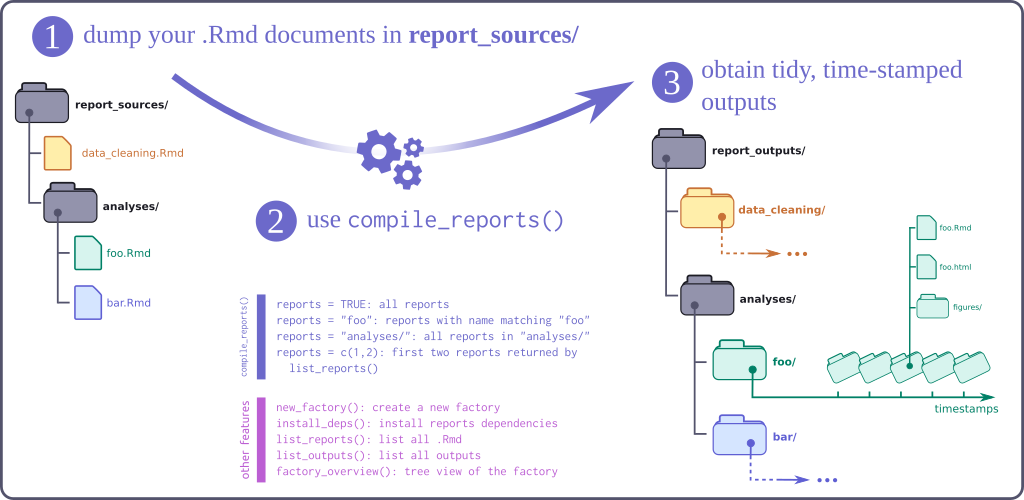
{reportfactory} is a R package which facilitates a workflow for
compiling multiple .Rmd reports within a folder.
There a few key principles it adheres to:
- Simplicity Only focusses on the compilation of reports not data
management.
- Reproducible Time-stamped folder structure and customisable
subfolder make viewing the same report over time a breeze.
- Time-saving Easy convenience functions to reports based on regular
expressions.
Installing the package
To install the development version of the package, use:
remotes::install_github("reconhub/reportfactory")
Quick start
Step 1 - Create a new factory
Create and open a new factory. Here, we create the factory with mostly
the default settings but stay in our current working directory (set
move_in to TRUE to switch directories).
library(reportfactory)
new_factory("my_factory", path = tempdir())
Step 2 - Add your reports
Here we’ve already created some with most of the default arguments being
set to TRUE (the default). These default settings include both an
example report and some associated data
(report_sources/example_report.Rmd and data/raw/example_data.csv).
The helper functions below show the state of the factory.
list_reports() # list all available report sources
#> example_report.Rmd
list_deps() # list all of the dependencies of the reports
#> [1] "here" "incidence2"
list_outputs() # currently empty
#> character(0)
Step 3 - Compile report(s)
The compile_reports() function can be used to compile a report using
regular expressions matched against the full filename of reports within
the factory.
This ability to use of regular expressions is useful when you’re
actively working on developing your reports but once the factory is
setup we recommend passing full filenames to the function so it is
always clear what will be built.
compile_reports(
reports = "example_report.Rmd"
)
#> >>> Compiling report: example_report
#> All done!
Use list_ouputs() to view the report outputs.
list_outputs()
#> example_report/2020-12-02_T21-42-07/example_report.Rmd
#> example_report/2020-12-02_T21-42-07/example_report.html
compile_reports() can also be used to pass a set of parameters to use
with a parameterised report (here we use a subfolder argument to
distinguish the parameterised reports).
compile_reports(
reports = "example_report.Rmd",
params = list(grouped_plot = FALSE),
subfolder = "regional"
)
#> >>> Compiling report: example_report
#> - with parameters: grouped_plot = FALSE
#> All done!
list_outputs()
#> example_report/2020-12-02_T21-42-07/example_report.Rmd
#> example_report/2020-12-02_T21-42-07/example_report.html
#> example_report/regional/2020-12-02_T21-42-08/example_report.Rmd
#> example_report/regional/2020-12-02_T21-42-08/example_report.html
If you want to have an overview of your entire factory then you can use
the fs package and the dir_tree function:
fs::dir_tree()
#> .
#> ├── README.md
#> ├── data
#> │ ├── clean
#> │ └── raw
#> │ └── example_data.csv
#> ├── factory_config
#> ├── outputs
#> │ └── example_report
#> │ ├── 2020-12-02_T21-42-07
#> │ │ ├── example_report.Rmd
#> │ │ └── example_report.html
#> │ └── regional
#> │ └── 2020-12-02_T21-42-08
#> │ ├── example_report.Rmd
#> │ └── example_report.html
#> ├── report_sources
#> │ └── example_report.Rmd
#> └── scripts
Contributing guidelines
Contributions are welcome via pull requests.
Code of Conduct
Please note that the reportfactory project is released with a
Contributor Code of
Conduct.
By contributing to this project, you agree to abide by its terms.
tjtnew/reportfactory documentation built on Dec. 31, 2020, 8:40 a.m.
Welcome to reportfactory!
NOTE
This version of {reportfactory} works in a very different way to the previous unreleased version. For those already using {reportfactory} in their pipelines you can obtain the old version using the {remotes} package:
remotes::install_github("reconhub/reportfactory@old_version")
You can also download it directly from https://github.com/reconhub/reportfactory/releases/tag/old_version.
reportfactory in a nutshell
{reportfactory} is a R package which facilitates a workflow for
compiling multiple .Rmd reports within a folder.
There a few key principles it adheres to:
- Simplicity Only focusses on the compilation of reports not data management.
- Reproducible Time-stamped folder structure and customisable subfolder make viewing the same report over time a breeze.
- Time-saving Easy convenience functions to reports based on regular expressions.

Installing the package
To install the development version of the package, use:
remotes::install_github("reconhub/reportfactory")
Quick start
Step 1 - Create a new factory
Create and open a new factory. Here, we create the factory with mostly
the default settings but stay in our current working directory (set
move_in to TRUE to switch directories).
library(reportfactory)
new_factory("my_factory", path = tempdir())
Step 2 - Add your reports
Here we’ve already created some with most of the default arguments being
set to TRUE (the default). These default settings include both an
example report and some associated data
(report_sources/example_report.Rmd and data/raw/example_data.csv).
The helper functions below show the state of the factory.
list_reports() # list all available report sources
#> example_report.Rmd
list_deps() # list all of the dependencies of the reports
#> [1] "here" "incidence2"
list_outputs() # currently empty
#> character(0)
Step 3 - Compile report(s)
The compile_reports() function can be used to compile a report using
regular expressions matched against the full filename of reports within
the factory.
This ability to use of regular expressions is useful when you’re actively working on developing your reports but once the factory is setup we recommend passing full filenames to the function so it is always clear what will be built.
compile_reports(
reports = "example_report.Rmd"
)
#> >>> Compiling report: example_report
#> All done!
Use list_ouputs() to view the report outputs.
list_outputs()
#> example_report/2020-12-02_T21-42-07/example_report.Rmd
#> example_report/2020-12-02_T21-42-07/example_report.html
compile_reports() can also be used to pass a set of parameters to use
with a parameterised report (here we use a subfolder argument to
distinguish the parameterised reports).
compile_reports(
reports = "example_report.Rmd",
params = list(grouped_plot = FALSE),
subfolder = "regional"
)
#> >>> Compiling report: example_report
#> - with parameters: grouped_plot = FALSE
#> All done!
list_outputs()
#> example_report/2020-12-02_T21-42-07/example_report.Rmd
#> example_report/2020-12-02_T21-42-07/example_report.html
#> example_report/regional/2020-12-02_T21-42-08/example_report.Rmd
#> example_report/regional/2020-12-02_T21-42-08/example_report.html
If you want to have an overview of your entire factory then you can use
the fs package and the dir_tree function:
fs::dir_tree()
#> .
#> ├── README.md
#> ├── data
#> │ ├── clean
#> │ └── raw
#> │ └── example_data.csv
#> ├── factory_config
#> ├── outputs
#> │ └── example_report
#> │ ├── 2020-12-02_T21-42-07
#> │ │ ├── example_report.Rmd
#> │ │ └── example_report.html
#> │ └── regional
#> │ └── 2020-12-02_T21-42-08
#> │ ├── example_report.Rmd
#> │ └── example_report.html
#> ├── report_sources
#> │ └── example_report.Rmd
#> └── scripts
Contributing guidelines
Contributions are welcome via pull requests.
Code of Conduct
Please note that the reportfactory project is released with a Contributor Code of Conduct. By contributing to this project, you agree to abide by its terms.
Add the following code to your website.
For more information on customizing the embed code, read Embedding Snippets.
