In lahuuki/DeconvoBuddies: Helper Functions for LIBD Deconvolution
knitr::opts_chunk$set(
collapse = TRUE,
comment = "#>",
crop = NULL ## Related to https://stat.ethz.ch/pipermail/bioc-devel/2020-April/016656.html
)
## Bib setup
library("RefManageR")
## Write bibliography information
bib <- c(
R = citation(),
BiocStyle = citation("BiocStyle")[1],
knitr = citation("knitr")[1],
RefManageR = citation("RefManageR")[1],
rmarkdown = citation("rmarkdown")[1],
sessioninfo = citation("sessioninfo")[1],
testthat = citation("testthat")[1],
DeconvoBuddies = citation("DeconvoBuddies")[1]
)
Introduction
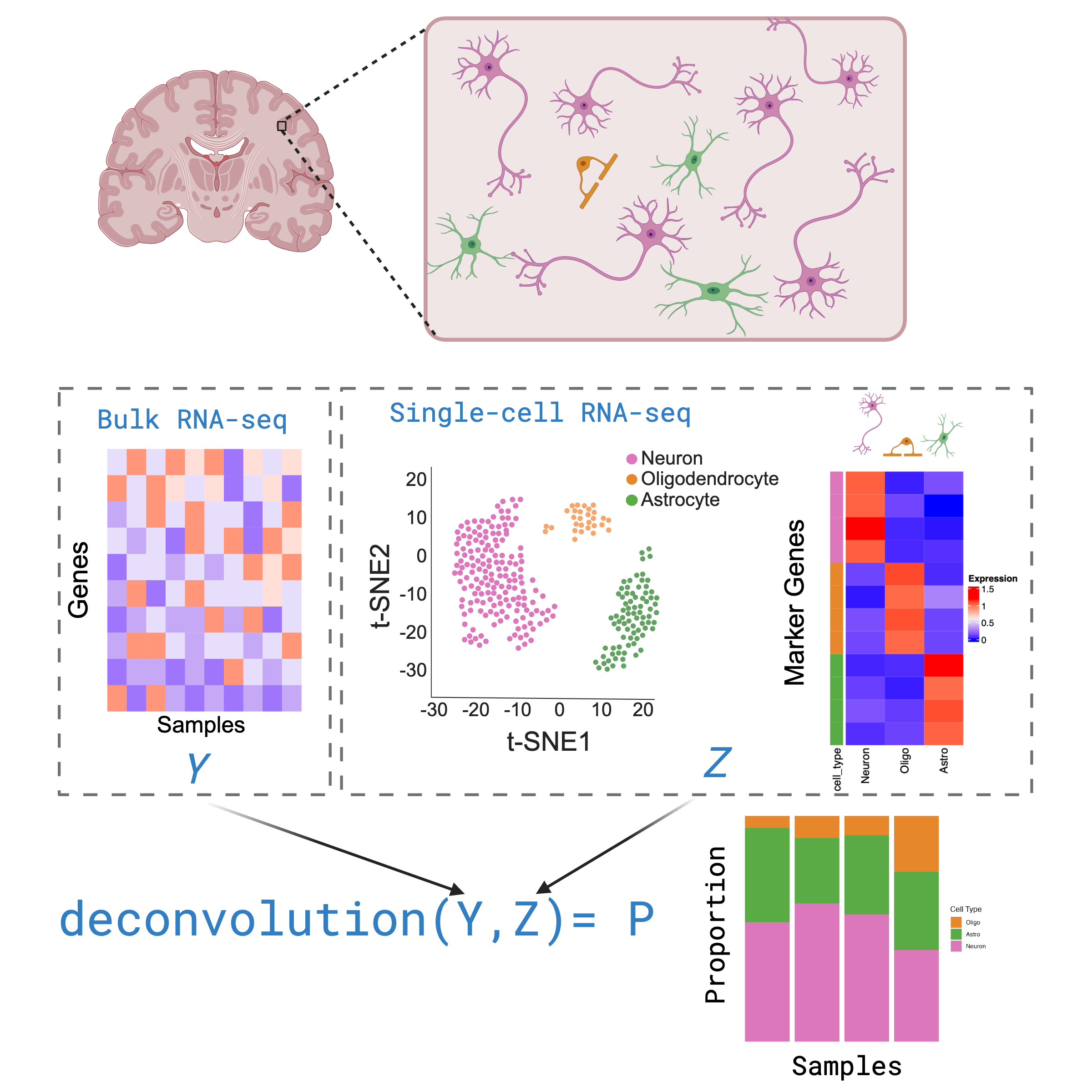
What is Deconvolution?
Inferring the composition of different cell types in a bulk RNA-seq
data
Deconvolution is a analysis that aims to calculate the proportion of
different cell types that make up a sample of bulk RNA-seq, based off of
cell type gene expression profiles in a single cell/nuclei RNA-seq
dataset.
Deconvolution Methods
There are 20+ published reference based deconvolution methods. Below are
a selection of 6 methods we tested in our deconvolution benchmark
study.
| Approach | Method | Citation | Availability |
|-------------------|-----------------|-----------------|---------------------|
| weighted least squares | DWLS | Tsoucas et al, Nature Comm, 2019 | R Package CRAN |
| Bias correction: Assay | Bisque | Jew et al, Nature Comm, 2020 | R Package GitHub |
| Bias correction: Source | MuSiC | Wang et al, Nature Communications, 2019 | R Package GitHub |
| Machine Learning | CIBERSORTx | Newman et al., Nature BioTech, 2019 | Webtool |
| Bayesian | BayesPrism | Chu et al., Nature Cancer, 2022 | Webtool/R Package |
| linear | Hspe | Hunt et al., Ann. Appl. Stat, 2021 | R package GitHub |
Goals of this Vignette
We will be demonstrating how to use DeconvoBuddies tools when applying
deconvolution with the Bisque package.
- Install and load required packages
- Download DLPFC RNA-seq data, and reference snRNA-seq data
- Find marker genes with
DeconvoBuddies tools
- Run deconvolution with
BisqueRNA
- Explore deconvolution output and create composition plots with
DeconvoBuddies tools
- Check proportion against RNAScope estimated proportions
Video Tutorial
Linked is a video from a presentation of an earlier version of this tutorial
from our LIBD Rstats club.
Basics
1. Install and load required packages
R is an open-source statistical environment which can be easily
modified to enhance its functionality via packages.
r Biocpkg("DeconvoBuddies") is a R package available via the
Bioconductor repository for packages. R can
be installed on any operating system from
CRAN after which you can install
r Biocpkg("DeconvoBuddies") by using the following commands in your
R session:
Install DeconvoBuddies
if (!requireNamespace("BiocManager", quietly = TRUE)) {
install.packages("BiocManager")
}
BiocManager::install("DeconvoBuddies")
## Check that you have a valid Bioconductor installation
BiocManager::valid()
Load Other Packages
Let's load the packages we'll be using in this vignette.
## Packages for different types of RNA-seq data structures in R
library("SummarizedExperiment")
library("SingleCellExperiment")
library("Biobase")
## For downloading data
library("spatialLIBD")
## For running deconvolution
library("BisqueRNA")
## Other helper packages for this vignette
library("dplyr")
library("tidyr")
library("tibble")
library("ggplot2")
## Our main package
library("DeconvoBuddies")
2. Download DLPFC RNA-seq data, and reference snRNA-seq data.
Bulk RNA-seq data
Access the 110 sample Human DLPFC bulk RNA-seq dataset for LIBD described in more detail here. These
samples\
are from 19 tissue blocks, and 10 neurotypical adult donors. Samples
were sequenced with two different library_types (polyA and
RiboZeroGold), and three different RNA_extraction (Cyto, Total, Nuc). There are in total n=110 samples after quality control.
## use fetch deconvo data to load rse_gene
rse_gene <- fetch_deconvo_data("rse_gene")
rse_gene
# lobstr::obj_size(rse_gene)
# 41.16 MB
## Use gene "Symbol" as identifiers for the genes in rownames(rse_gene)
rownames(rse_gene) <- rowData(rse_gene)$Symbol
## bulk RNA seq samples were sequenced with different library types,
## and RNA extractions
table(rse_gene$library_type, rse_gene$library_prep)
Reference snRNA-seq data
This data is paired with a single nucleus RNA-seq data set from
spatialLIBD. This dataset can be accessed with
spatialLIBD::fetch_data().
## Use spatialLIBD to fetch the snRNA-seq dataset used in this project
sce_path_zip <- fetch_deconvo_data("sce")
## unzip and load the data
sce_path <- unzip(sce_path_zip, exdir = tempdir())
sce <- HDF5Array::loadHDF5SummarizedExperiment(
file.path(tempdir(), "sce_DLPFC_annotated")
)
# lobstr::obj_size(sce)
# 172.28 MB
## exclude Ambiguous cell type
sce <- sce[, sce$cellType_broad_hc != "Ambiguous"]
sce$cellType_broad_hc <- droplevels(sce$cellType_broad_hc)
## Check the number of genes by the number of nuclei that we
## have to work with:
dim(sce)
## Check the broad cell type distribution
table(sce$cellType_broad_hc)
## We're going to subset to the first 5k genes to save memory
## just for this example. You wouldn't do this on a full analysis.
sce <- sce[seq_len(5000), ]
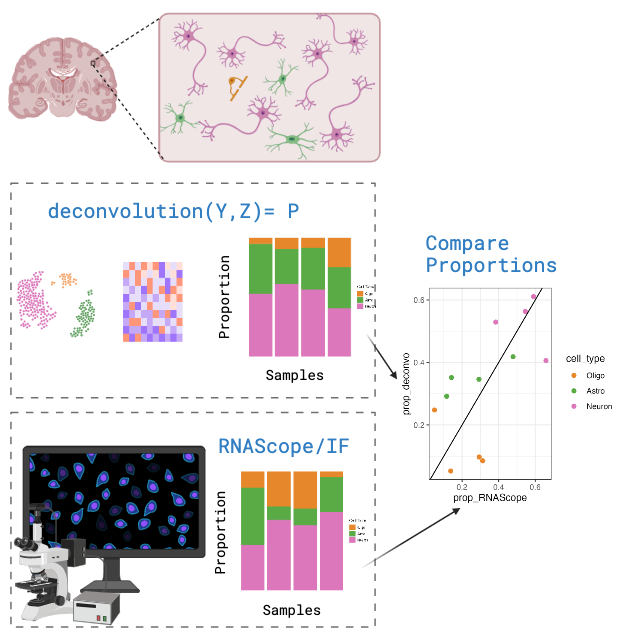
Orthogonal Cell Type Proportion from RNAScope/IF
An alternative method for calculating cell type proportions is through
imaging a slice of tissue with cell type probes using single molecule fluorescent in situ hybridization (smFISH) experiments performed with RNAScope/IF (ImmunoFluorescence). Then
analyse the image to count cells and annotate them by cell type. In this
study we used HALO from Indica Labs for this step.
The cell type proportions from the RNAScope/IF experiment will be used
to evaluate the accuracy of cell type proportion estimates.
The RNAScope/IF proportion data is stored as a data.frame object in
DeconvoBuddies::RNAScope_prop.
Key columns in RNAScope_prop:
-
SAMPLE_ID: DLPFC Tissue block + RNAScope combination.
-
Sample : DLFPC Tissue block (Donor BrNum + DLPFC position).
-
cell_type : The cell type measured.
-
n_cell : the number of cells counted for the Sample and cell type.
-
prop : the calculated cell type proportion from n_cell
# Access the RNAScope proportion data.frame
data("RNAScope_prop")
head(RNAScope_prop)
## plot the RNAScope compositions
plot_composition_bar(
prop_long = RNAScope_prop,
sample_col = "SAMPLE_ID",
x_col = "SAMPLE_ID",
add_text = FALSE
) +
facet_wrap(~Combo, nrow = 2, scales = "free_x")
Above we can see the cell proportions for each of the samples in either the Circle or the Star combination of RNAScope/IF probes. Each combination of RNAScope/IF probes was able to assess different sets of cell types. Two of them had to be used to measure the number of cell types studied in this case as there are limits on how many unique probes you can measure in a given RNAScope/IF experiment. For more details about the RNAScope/IF combinations, check the paper describing this study.
3. Select Marker Genes
Marker genes are genes with high expression in one cell type and low
expression in other cell types, or "cell-type specific" expression.
These genes can be used to learn more about the identity and function of
cell types, but here we are interested in using a sets of cell type
specific marker genes to reduce noise in deconvolution and increase
accuracy.
We have developed a method for finding marker genes called the "Mean
Ratio". We calculate the MeanRatio for a target cell type for each
gene by dividing the mean expression of the target cell by the mean
expression of the next highest non-target cell type. Genes with the
highest MeanRatio values are selected as marker genes.
For a tutorial on marker gene selection check out Vignette: Finding Marker Genes with Deconvo Buddies.
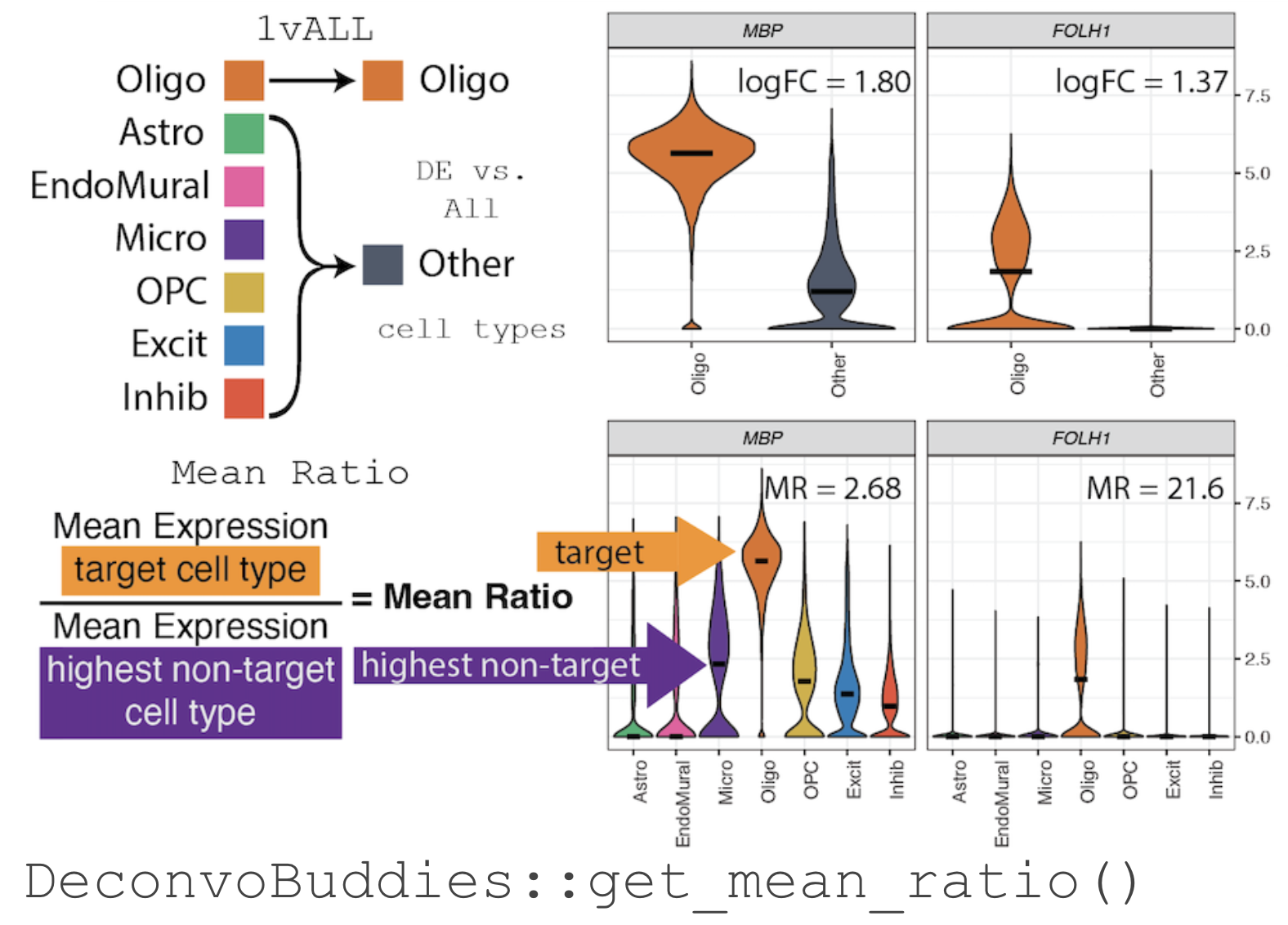
Use get_mean_ratio() to find marker genes.
The function DeconvoBuddies::get_mean_ratio() calculates the
MeanRatio and the rank of genes for a specified cell type annotation
in an SingleCellExperiment object.
# calculate the Mean Ratio of genes for each cell type
marker_stats <- get_mean_ratio(sce,
cellType_col = "cellType_broad_hc",
gene_ensembl = "gene_id",
gene_name = "gene_name"
)
# check the top gene ranked gene for each cell type
marker_stats |>
group_by(cellType.target) |>
slice(1)
The columns of this table are documented in detail at DeconvoBuddies::get_mean_ratio(). Though cellType.target lists the target cell type for which the MeanRatio is being calculated. It is the numerator of the MeanRatio. The cellType.2nd lists the cell type against which the target cell type is being compared. It is the denominator of the MeanRatio.
Plot the top marker genes
Use DeconvoBuddies plotting tools to quickly plot the gene expression
of the top 4 Excitatory neuron marker genes across the
cellType_broad_hc cell type annotations.
# plot expression across cell type the top 4 Excit marker genes
plot_marker_express(sce,
stats = marker_stats,
cell_type = "Excit",
cellType_col = "cellType_broad_hc",
rank_col = "MeanRatio.rank",
anno_col = "MeanRatio.anno",
gene_col = "gene"
)
Looks nice and cell type specific!
Note how plot_marker_express() lists the 2 cell types that are being compared that result in the specific numerical MeanRatio value being displayed. As we specified that our target cell type is "Excit" in our call to plot_marker_express(), the numerator is Excit in all the panels shown above.
Create a List of Marker Genes
With the MeanRatio calculated, we will select the top 25 highest Mean
Ratio genes for each cell type, that also exists in the bulk data
rse_gene.
# select top 25 marker genes for each cell type, that are also in rse_gene
marker_genes <- marker_stats |>
filter(MeanRatio.rank <= 25 & gene %in% rownames(rse_gene))
# check how many genes for each cell type (some genes are not in both datasets)
marker_genes |> count(cellType.target)
# create a vector of marker genes to subset data before deconvolution
marker_genes <- marker_genes |> pull(gene)
4. Prep Data and Run Bisque
Bisque is an R package for cell
type deconvolution. In our deconvolution benchmark, we found it was a
top performing method. Below we will briefly show how to run Bisque's
"reference based decomposition (deconvolution)".
Prepare data
To run Bisque the snRNA-seq and bulk data must first be converted to
Biobase::ExpressionSet() format. We will subset our data to our selected
MeanRatio marker genes.
The snRNA-seq data must also be filtered for cells with no counts across
marker genes.
## convert bulk data to Expression set, sub-setting to marker genes
## include sample ID
exp_set_bulk <- Biobase::ExpressionSet(
assayData = assays(rse_gene[marker_genes, ])$counts,
phenoData = AnnotatedDataFrame(
as.data.frame(colData(rse_gene))[c("SAMPLE_ID")]
)
)
## convert snRNA-seq data to Expression set, sub-setting to marker genes
## include cell type and donor information
exp_set_sce <- Biobase::ExpressionSet(
assayData = as.matrix(assays(sce[marker_genes, ])$counts),
phenoData = AnnotatedDataFrame(
as.data.frame(colData(sce))[, c("cellType_broad_hc", "BrNum")]
)
)
## check for nuclei with 0 marker expression
zero_cell_filter <- colSums(exprs(exp_set_sce)) != 0
message("Exclude ", sum(!zero_cell_filter), " cells")
exp_set_sce <- exp_set_sce[, zero_cell_filter]
Run Bisque
Bisque needs the bulk and single cell ExpressionSet we prepared
above, plus columns in the single cell data that specify the cell type
annotation to use cellType_broad_hc and donor id (BrNum in this
data).
## Run Bisque with bulk and single cell ExpressionSet inputs
est_prop <- ReferenceBasedDecomposition(
bulk.eset = exp_set_bulk,
sc.eset = exp_set_sce,
cell.types = "cellType_broad_hc",
subject.names = "BrNum",
use.overlap = FALSE
)
Explore Output
Bisque predicts the proportion of the cell types in cellType_broad_hc
for each sample in the bulk data.
## Examine the output from Bisque, transpose to make it easier to work with
est_prop$bulk.props <- t(est_prop$bulk.props)
## sample x cell type matrix
head(est_prop$bulk.props)
5. Explore deconvolution output and create composition plots with DeconvoBuddies tools
To visualize the cell type proportion predictions, we can plot cell type
composition bar plots with DeconvoBuddies::plot_composition_bar(),
either the prediction for each sample, or the average proportion over a
group of samples.
## add Phenotype data to proportion estimates
pd <- colData(rse_gene) |>
as.data.frame() |>
select(SAMPLE_ID, Sample, library_combo)
## make proportion estimates long so they are ggplot2 friendly
prop_long <- est_prop$bulk.props |>
as.data.frame() |>
tibble::rownames_to_column("SAMPLE_ID") |>
tidyr::pivot_longer(!SAMPLE_ID, names_to = "cell_type", values_to = "prop") |>
left_join(pd)
## create composition bar plots
## for all library preparations by sample n=110
## Remove the SAMPLE_ID names since they are very long using ggplot2::theme()
plot_composition_bar(
prop_long = prop_long,
sample_col = "SAMPLE_ID",
x_col = "SAMPLE_ID",
add_text = FALSE
) +
theme(axis.text.x = element_blank(), axis.ticks.x = element_blank())
## Average by brain donor
plot_composition_bar(
prop_long = prop_long,
sample_col = "SAMPLE_ID",
x_col = "Sample",
add_text = FALSE
)
## Each brain donor has up to 6 unique RNA library type and RNA extraction
## combinations
table(prop_long$Sample) / length(unique(prop_long$cell_type))
## Here are the 6 "SAMPLE_ID" values for brain donor with ID "Br8667_mid"
unique(prop_long$SAMPLE_ID[prop_long$Sample == "Br8667_mid"])
This is a more complex scenario than the one from the introductory vignette where we were using random data. The first plot shows each of the n=110 bulk RNA-seq samples we have. The second plot shows the composition using the average across the 6 RNA library types and RNA extractions for each brain donor.
6. Check proportion against RNAScope/IF estimated proportions
Note to compare the deconvolution results to the RNAScope/IF proportions,
Oligo and OPC need to be added together.
## Combine Oligo and OPC into OligoOPC
prop_long_opc <- prop_long |>
mutate(cell_type = gsub("Oligo|OPC", "OligoOPC", cell_type)) |>
group_by(SAMPLE_ID, Sample, library_combo, cell_type) |>
summarize(prop = sum(prop)) |>
ungroup()
prop_long_opc |> count(cell_type)
## Join RNAScope/IF and Bisque cell type proportions
prop_compare <- prop_long_opc |>
inner_join(
RNAScope_prop |>
select(Sample, cell_type, prop_RNAScope = prop, prop_sn),
by = c("Sample", "cell_type")
)
We can now calculate the correlation plot a scatter plot of the proportions. Note that you can change the type of correlation algorithm used in the cor() function. The default method is "pearson".
## compute correlation with RNAScope/IF proportions
cor(prop_compare$prop, prop_compare$prop_RNAScope)
## Scatter plot with RNAScope/IF proportions
prop_compare |>
ggplot(aes(x = prop_RNAScope, y = prop, color = cell_type, shape = library_combo)) +
geom_point() +
geom_abline()
## correlation with snRNA-seq proportion
cor(prop_compare$prop, prop_compare$prop_sn)
## Scatter plot with RNAScope/IF proportions
prop_compare |>
ggplot(aes(x = prop_sn, y = prop, color = cell_type, shape = library_combo)) +
geom_point() +
geom_abline()
In the first plot we can see how Bisque overestimates the proportion of excitatory neurons (Excit) when compared against RNAScope/IF as all Excit points are higher than the diagonal line shown in black.
In the second plot we can see how Bisque proportions are closer to the snRNA-seq proportions. After all, given the challenges in generating orthogonal cell type proportion data, Bisque and other deconvolution methods were developed by comparing against simulated data, sometimes using pseudo-bulk sc/snRNA-seq data.
7. How to run deconvolution with hspe
hspe (formerly called dtangle) is another R package for deconvolution. It
was also a top performing method in our deconvolution benchmark.
hspe is downloadable from GitHub but
can't be shown on this vignette as Bioconductor packages cannot use packages from GitHub.
Below we show some example code to prepare input data and run hspe (not run
here):
if (FALSE) {
## Install hspe
# if (!requireNamespace("hspe", quietly = TRUE)) {
# ## Install version 0.1 which is the one listed on the main documentation
# ## at https://github.com/gjhunt/hspe/tree/main?tab=readme-ov-file#software
# remotes::install_url("https://github.com/gjhunt/hspe/raw/main/hspe_0.1.tar.gz")
# ## Alternatively, install from the latest version on GitHub with:
# # remotes::install_github("gjhunt/hspe", subdir = "lib_hspe")
#
# ## As of 2024-08-23, it's been 3 years since files were last modified
# ## at https://github.com/gjhunt/hspe/tree/main/lib_hspe.
# }
# library("hspe")
# pseudobulk the sce data by sample + cell type
sce_pb <- spatialLIBD::registration_pseudobulk(sce,
var_registration = "cellType_broad_hc",
var_sample_id = "Sample"
)
## extract the gene expression from the bulk rse_gene
mixture_samples <- t(assays(rse_gene)$logcounts)
mixture_samples[1:5, 1:5]
## create a vector of indexes of the different cell types
pure_samples <- rafalib::splitit(sce_pb$cellType_broad_hc)
## extract the the pseudobulked logcounts
reference_samples <- t(assays(sce_pb)$logcounts)
reference_samples[1:5, 1:5]
## check the number of genes match in the bulk (mixture) and single cell (reference)
ncol(mixture_samples) == ncol(reference_samples)
## run hspe
est_prop_hspe <- hspe(
Y = mixture_samples,
reference = reference_samples,
pure_samples = pure_samples,
markers = marker_genes,
seed = 10524
)
}
Conclusion
In this vignette we have demonstrated some of the functions and data in
the DeconvoBuddies package, and how to use them in a deconvolution
workflow to predict cell type proportions. We used real data from a study
on human brain.
Reproducibility
The r Biocpkg("DeconvoBuddies") package
r Citep(bib[["DeconvoBuddies"]]) was made possible thanks to:
- R
r Citep(bib[["R"]])
r Biocpkg("BiocStyle") r Citep(bib[["BiocStyle"]])r CRANpkg("knitr") r Citep(bib[["knitr"]])r CRANpkg("RefManageR") r Citep(bib[["RefManageR"]])r CRANpkg("rmarkdown") r Citep(bib[["rmarkdown"]])r CRANpkg("sessioninfo") r Citep(bib[["sessioninfo"]])r CRANpkg("testthat") r Citep(bib[["testthat"]])
This package was developed using r BiocStyle::Biocpkg("biocthis").
R session information.
## Session info
library("sessioninfo")
options(width = 120)
session_info()
Bibliography
This vignette was generated using r Biocpkg("BiocStyle")
r Citep(bib[["BiocStyle"]]) with r CRANpkg("knitr")
r Citep(bib[["knitr"]]) and r CRANpkg("rmarkdown")
r Citep(bib[["rmarkdown"]]) running behind the scenes.
Citations made with r CRANpkg("RefManageR")
r Citep(bib[["RefManageR"]]).
## Print bibliography
PrintBibliography(bib, .opts = list(hyperlink = "to.doc", style = "html"))
lahuuki/DeconvoBuddies documentation built on March 29, 2025, 5:24 p.m.
knitr::opts_chunk$set( collapse = TRUE, comment = "#>", crop = NULL ## Related to https://stat.ethz.ch/pipermail/bioc-devel/2020-April/016656.html )
## Bib setup library("RefManageR") ## Write bibliography information bib <- c( R = citation(), BiocStyle = citation("BiocStyle")[1], knitr = citation("knitr")[1], RefManageR = citation("RefManageR")[1], rmarkdown = citation("rmarkdown")[1], sessioninfo = citation("sessioninfo")[1], testthat = citation("testthat")[1], DeconvoBuddies = citation("DeconvoBuddies")[1] )
Introduction
What is Deconvolution?
Inferring the composition of different cell types in a bulk RNA-seq data
Deconvolution is a analysis that aims to calculate the proportion of different cell types that make up a sample of bulk RNA-seq, based off of cell type gene expression profiles in a single cell/nuclei RNA-seq dataset.

Deconvolution Methods
There are 20+ published reference based deconvolution methods. Below are a selection of 6 methods we tested in our deconvolution benchmark study.
| Approach | Method | Citation | Availability | |-------------------|-----------------|-----------------|---------------------| | weighted least squares | DWLS | Tsoucas et al, Nature Comm, 2019 | R Package CRAN | | Bias correction: Assay | Bisque | Jew et al, Nature Comm, 2020 | R Package GitHub | | Bias correction: Source | MuSiC | Wang et al, Nature Communications, 2019 | R Package GitHub | | Machine Learning | CIBERSORTx | Newman et al., Nature BioTech, 2019 | Webtool | | Bayesian | BayesPrism | Chu et al., Nature Cancer, 2022 | Webtool/R Package | | linear | Hspe | Hunt et al., Ann. Appl. Stat, 2021 | R package GitHub |
Goals of this Vignette
We will be demonstrating how to use DeconvoBuddies tools when applying
deconvolution with the Bisque package.
- Install and load required packages
- Download DLPFC RNA-seq data, and reference snRNA-seq data
- Find marker genes with
DeconvoBuddiestools - Run deconvolution with
BisqueRNA - Explore deconvolution output and create composition plots with
DeconvoBuddiestools - Check proportion against RNAScope estimated proportions
Video Tutorial
Linked is a video from a presentation of an earlier version of this tutorial from our LIBD Rstats club.
Basics
1. Install and load required packages
R is an open-source statistical environment which can be easily
modified to enhance its functionality via packages.
r Biocpkg("DeconvoBuddies") is a R package available via the
Bioconductor repository for packages. R can
be installed on any operating system from
CRAN after which you can install
r Biocpkg("DeconvoBuddies") by using the following commands in your
R session:
Install DeconvoBuddies
if (!requireNamespace("BiocManager", quietly = TRUE)) { install.packages("BiocManager") } BiocManager::install("DeconvoBuddies") ## Check that you have a valid Bioconductor installation BiocManager::valid()
Load Other Packages
Let's load the packages we'll be using in this vignette.
## Packages for different types of RNA-seq data structures in R library("SummarizedExperiment") library("SingleCellExperiment") library("Biobase") ## For downloading data library("spatialLIBD") ## For running deconvolution library("BisqueRNA") ## Other helper packages for this vignette library("dplyr") library("tidyr") library("tibble") library("ggplot2") ## Our main package library("DeconvoBuddies")
2. Download DLPFC RNA-seq data, and reference snRNA-seq data.
Bulk RNA-seq data
Access the 110 sample Human DLPFC bulk RNA-seq dataset for LIBD described in more detail here. These
samples\
are from 19 tissue blocks, and 10 neurotypical adult donors. Samples
were sequenced with two different library_types (polyA and
RiboZeroGold), and three different RNA_extraction (Cyto, Total, Nuc). There are in total n=110 samples after quality control.
## use fetch deconvo data to load rse_gene rse_gene <- fetch_deconvo_data("rse_gene") rse_gene # lobstr::obj_size(rse_gene) # 41.16 MB ## Use gene "Symbol" as identifiers for the genes in rownames(rse_gene) rownames(rse_gene) <- rowData(rse_gene)$Symbol ## bulk RNA seq samples were sequenced with different library types, ## and RNA extractions table(rse_gene$library_type, rse_gene$library_prep)
Reference snRNA-seq data
This data is paired with a single nucleus RNA-seq data set from
spatialLIBD. This dataset can be accessed with
spatialLIBD::fetch_data().
## Use spatialLIBD to fetch the snRNA-seq dataset used in this project sce_path_zip <- fetch_deconvo_data("sce") ## unzip and load the data sce_path <- unzip(sce_path_zip, exdir = tempdir()) sce <- HDF5Array::loadHDF5SummarizedExperiment( file.path(tempdir(), "sce_DLPFC_annotated") ) # lobstr::obj_size(sce) # 172.28 MB ## exclude Ambiguous cell type sce <- sce[, sce$cellType_broad_hc != "Ambiguous"] sce$cellType_broad_hc <- droplevels(sce$cellType_broad_hc) ## Check the number of genes by the number of nuclei that we ## have to work with: dim(sce) ## Check the broad cell type distribution table(sce$cellType_broad_hc) ## We're going to subset to the first 5k genes to save memory ## just for this example. You wouldn't do this on a full analysis. sce <- sce[seq_len(5000), ]
Orthogonal Cell Type Proportion from RNAScope/IF
An alternative method for calculating cell type proportions is through imaging a slice of tissue with cell type probes using single molecule fluorescent in situ hybridization (smFISH) experiments performed with RNAScope/IF (ImmunoFluorescence). Then analyse the image to count cells and annotate them by cell type. In this study we used HALO from Indica Labs for this step.
The cell type proportions from the RNAScope/IF experiment will be used to evaluate the accuracy of cell type proportion estimates.

The RNAScope/IF proportion data is stored as a data.frame object in
DeconvoBuddies::RNAScope_prop.
Key columns in RNAScope_prop:
-
SAMPLE_ID: DLPFC Tissue block + RNAScope combination. -
Sample: DLFPC Tissue block (Donor BrNum + DLPFC position). -
cell_type: The cell type measured. -
n_cell: the number of cells counted for the Sample and cell type. -
prop: the calculated cell type proportion from n_cell
# Access the RNAScope proportion data.frame data("RNAScope_prop") head(RNAScope_prop) ## plot the RNAScope compositions plot_composition_bar( prop_long = RNAScope_prop, sample_col = "SAMPLE_ID", x_col = "SAMPLE_ID", add_text = FALSE ) + facet_wrap(~Combo, nrow = 2, scales = "free_x")
Above we can see the cell proportions for each of the samples in either the Circle or the Star combination of RNAScope/IF probes. Each combination of RNAScope/IF probes was able to assess different sets of cell types. Two of them had to be used to measure the number of cell types studied in this case as there are limits on how many unique probes you can measure in a given RNAScope/IF experiment. For more details about the RNAScope/IF combinations, check the paper describing this study.
3. Select Marker Genes
Marker genes are genes with high expression in one cell type and low expression in other cell types, or "cell-type specific" expression. These genes can be used to learn more about the identity and function of cell types, but here we are interested in using a sets of cell type specific marker genes to reduce noise in deconvolution and increase accuracy.
We have developed a method for finding marker genes called the "Mean Ratio". We calculate the MeanRatio for a target cell type for each gene by dividing the mean expression of the target cell by the mean expression of the next highest non-target cell type. Genes with the highest MeanRatio values are selected as marker genes.
For a tutorial on marker gene selection check out Vignette: Finding Marker Genes with Deconvo Buddies.

Use get_mean_ratio() to find marker genes.
The function DeconvoBuddies::get_mean_ratio() calculates the
MeanRatio and the rank of genes for a specified cell type annotation
in an SingleCellExperiment object.
# calculate the Mean Ratio of genes for each cell type marker_stats <- get_mean_ratio(sce, cellType_col = "cellType_broad_hc", gene_ensembl = "gene_id", gene_name = "gene_name" ) # check the top gene ranked gene for each cell type marker_stats |> group_by(cellType.target) |> slice(1)
The columns of this table are documented in detail at DeconvoBuddies::get_mean_ratio(). Though cellType.target lists the target cell type for which the MeanRatio is being calculated. It is the numerator of the MeanRatio. The cellType.2nd lists the cell type against which the target cell type is being compared. It is the denominator of the MeanRatio.
Plot the top marker genes
Use DeconvoBuddies plotting tools to quickly plot the gene expression
of the top 4 Excitatory neuron marker genes across the
cellType_broad_hc cell type annotations.
# plot expression across cell type the top 4 Excit marker genes plot_marker_express(sce, stats = marker_stats, cell_type = "Excit", cellType_col = "cellType_broad_hc", rank_col = "MeanRatio.rank", anno_col = "MeanRatio.anno", gene_col = "gene" )
Looks nice and cell type specific!
Note how plot_marker_express() lists the 2 cell types that are being compared that result in the specific numerical MeanRatio value being displayed. As we specified that our target cell type is "Excit" in our call to plot_marker_express(), the numerator is Excit in all the panels shown above.
Create a List of Marker Genes
With the MeanRatio calculated, we will select the top 25 highest Mean
Ratio genes for each cell type, that also exists in the bulk data
rse_gene.
# select top 25 marker genes for each cell type, that are also in rse_gene marker_genes <- marker_stats |> filter(MeanRatio.rank <= 25 & gene %in% rownames(rse_gene)) # check how many genes for each cell type (some genes are not in both datasets) marker_genes |> count(cellType.target) # create a vector of marker genes to subset data before deconvolution marker_genes <- marker_genes |> pull(gene)
4. Prep Data and Run Bisque
Bisque is an R package for cell
type deconvolution. In our deconvolution benchmark, we found it was a
top performing method. Below we will briefly show how to run Bisque's
"reference based decomposition (deconvolution)".
Prepare data
To run Bisque the snRNA-seq and bulk data must first be converted to
Biobase::ExpressionSet() format. We will subset our data to our selected
MeanRatio marker genes.
The snRNA-seq data must also be filtered for cells with no counts across marker genes.
## convert bulk data to Expression set, sub-setting to marker genes ## include sample ID exp_set_bulk <- Biobase::ExpressionSet( assayData = assays(rse_gene[marker_genes, ])$counts, phenoData = AnnotatedDataFrame( as.data.frame(colData(rse_gene))[c("SAMPLE_ID")] ) ) ## convert snRNA-seq data to Expression set, sub-setting to marker genes ## include cell type and donor information exp_set_sce <- Biobase::ExpressionSet( assayData = as.matrix(assays(sce[marker_genes, ])$counts), phenoData = AnnotatedDataFrame( as.data.frame(colData(sce))[, c("cellType_broad_hc", "BrNum")] ) ) ## check for nuclei with 0 marker expression zero_cell_filter <- colSums(exprs(exp_set_sce)) != 0 message("Exclude ", sum(!zero_cell_filter), " cells") exp_set_sce <- exp_set_sce[, zero_cell_filter]
Run Bisque
Bisque needs the bulk and single cell ExpressionSet we prepared
above, plus columns in the single cell data that specify the cell type
annotation to use cellType_broad_hc and donor id (BrNum in this
data).
## Run Bisque with bulk and single cell ExpressionSet inputs est_prop <- ReferenceBasedDecomposition( bulk.eset = exp_set_bulk, sc.eset = exp_set_sce, cell.types = "cellType_broad_hc", subject.names = "BrNum", use.overlap = FALSE )
Explore Output
Bisque predicts the proportion of the cell types in cellType_broad_hc
for each sample in the bulk data.
## Examine the output from Bisque, transpose to make it easier to work with est_prop$bulk.props <- t(est_prop$bulk.props) ## sample x cell type matrix head(est_prop$bulk.props)
5. Explore deconvolution output and create composition plots with DeconvoBuddies tools
To visualize the cell type proportion predictions, we can plot cell type
composition bar plots with DeconvoBuddies::plot_composition_bar(),
either the prediction for each sample, or the average proportion over a
group of samples.
## add Phenotype data to proportion estimates pd <- colData(rse_gene) |> as.data.frame() |> select(SAMPLE_ID, Sample, library_combo) ## make proportion estimates long so they are ggplot2 friendly prop_long <- est_prop$bulk.props |> as.data.frame() |> tibble::rownames_to_column("SAMPLE_ID") |> tidyr::pivot_longer(!SAMPLE_ID, names_to = "cell_type", values_to = "prop") |> left_join(pd) ## create composition bar plots ## for all library preparations by sample n=110 ## Remove the SAMPLE_ID names since they are very long using ggplot2::theme() plot_composition_bar( prop_long = prop_long, sample_col = "SAMPLE_ID", x_col = "SAMPLE_ID", add_text = FALSE ) + theme(axis.text.x = element_blank(), axis.ticks.x = element_blank()) ## Average by brain donor plot_composition_bar( prop_long = prop_long, sample_col = "SAMPLE_ID", x_col = "Sample", add_text = FALSE ) ## Each brain donor has up to 6 unique RNA library type and RNA extraction ## combinations table(prop_long$Sample) / length(unique(prop_long$cell_type)) ## Here are the 6 "SAMPLE_ID" values for brain donor with ID "Br8667_mid" unique(prop_long$SAMPLE_ID[prop_long$Sample == "Br8667_mid"])
This is a more complex scenario than the one from the introductory vignette where we were using random data. The first plot shows each of the n=110 bulk RNA-seq samples we have. The second plot shows the composition using the average across the 6 RNA library types and RNA extractions for each brain donor.
6. Check proportion against RNAScope/IF estimated proportions
Note to compare the deconvolution results to the RNAScope/IF proportions, Oligo and OPC need to be added together.
## Combine Oligo and OPC into OligoOPC prop_long_opc <- prop_long |> mutate(cell_type = gsub("Oligo|OPC", "OligoOPC", cell_type)) |> group_by(SAMPLE_ID, Sample, library_combo, cell_type) |> summarize(prop = sum(prop)) |> ungroup() prop_long_opc |> count(cell_type) ## Join RNAScope/IF and Bisque cell type proportions prop_compare <- prop_long_opc |> inner_join( RNAScope_prop |> select(Sample, cell_type, prop_RNAScope = prop, prop_sn), by = c("Sample", "cell_type") )
We can now calculate the correlation plot a scatter plot of the proportions. Note that you can change the type of correlation algorithm used in the cor() function. The default method is "pearson".
## compute correlation with RNAScope/IF proportions cor(prop_compare$prop, prop_compare$prop_RNAScope) ## Scatter plot with RNAScope/IF proportions prop_compare |> ggplot(aes(x = prop_RNAScope, y = prop, color = cell_type, shape = library_combo)) + geom_point() + geom_abline() ## correlation with snRNA-seq proportion cor(prop_compare$prop, prop_compare$prop_sn) ## Scatter plot with RNAScope/IF proportions prop_compare |> ggplot(aes(x = prop_sn, y = prop, color = cell_type, shape = library_combo)) + geom_point() + geom_abline()
In the first plot we can see how Bisque overestimates the proportion of excitatory neurons (Excit) when compared against RNAScope/IF as all Excit points are higher than the diagonal line shown in black.
In the second plot we can see how Bisque proportions are closer to the snRNA-seq proportions. After all, given the challenges in generating orthogonal cell type proportion data, Bisque and other deconvolution methods were developed by comparing against simulated data, sometimes using pseudo-bulk sc/snRNA-seq data.
7. How to run deconvolution with hspe
hspe (formerly called dtangle) is another R package for deconvolution. It was also a top performing method in our deconvolution benchmark.
hspe is downloadable from GitHub but
can't be shown on this vignette as Bioconductor packages cannot use packages from GitHub.
Below we show some example code to prepare input data and run hspe (not run
here):
if (FALSE) { ## Install hspe # if (!requireNamespace("hspe", quietly = TRUE)) { # ## Install version 0.1 which is the one listed on the main documentation # ## at https://github.com/gjhunt/hspe/tree/main?tab=readme-ov-file#software # remotes::install_url("https://github.com/gjhunt/hspe/raw/main/hspe_0.1.tar.gz") # ## Alternatively, install from the latest version on GitHub with: # # remotes::install_github("gjhunt/hspe", subdir = "lib_hspe") # # ## As of 2024-08-23, it's been 3 years since files were last modified # ## at https://github.com/gjhunt/hspe/tree/main/lib_hspe. # } # library("hspe") # pseudobulk the sce data by sample + cell type sce_pb <- spatialLIBD::registration_pseudobulk(sce, var_registration = "cellType_broad_hc", var_sample_id = "Sample" ) ## extract the gene expression from the bulk rse_gene mixture_samples <- t(assays(rse_gene)$logcounts) mixture_samples[1:5, 1:5] ## create a vector of indexes of the different cell types pure_samples <- rafalib::splitit(sce_pb$cellType_broad_hc) ## extract the the pseudobulked logcounts reference_samples <- t(assays(sce_pb)$logcounts) reference_samples[1:5, 1:5] ## check the number of genes match in the bulk (mixture) and single cell (reference) ncol(mixture_samples) == ncol(reference_samples) ## run hspe est_prop_hspe <- hspe( Y = mixture_samples, reference = reference_samples, pure_samples = pure_samples, markers = marker_genes, seed = 10524 ) }
Conclusion
In this vignette we have demonstrated some of the functions and data in
the DeconvoBuddies package, and how to use them in a deconvolution
workflow to predict cell type proportions. We used real data from a study
on human brain.
Reproducibility
The r Biocpkg("DeconvoBuddies") package
r Citep(bib[["DeconvoBuddies"]]) was made possible thanks to:
- R
r Citep(bib[["R"]]) r Biocpkg("BiocStyle")r Citep(bib[["BiocStyle"]])r CRANpkg("knitr")r Citep(bib[["knitr"]])r CRANpkg("RefManageR")r Citep(bib[["RefManageR"]])r CRANpkg("rmarkdown")r Citep(bib[["rmarkdown"]])r CRANpkg("sessioninfo")r Citep(bib[["sessioninfo"]])r CRANpkg("testthat")r Citep(bib[["testthat"]])
This package was developed using r BiocStyle::Biocpkg("biocthis").
R session information.
## Session info library("sessioninfo") options(width = 120) session_info()
Bibliography
This vignette was generated using r Biocpkg("BiocStyle")
r Citep(bib[["BiocStyle"]]) with r CRANpkg("knitr")
r Citep(bib[["knitr"]]) and r CRANpkg("rmarkdown")
r Citep(bib[["rmarkdown"]]) running behind the scenes.
Citations made with r CRANpkg("RefManageR")
r Citep(bib[["RefManageR"]]).
## Print bibliography PrintBibliography(bib, .opts = list(hyperlink = "to.doc", style = "html"))
Add the following code to your website.
For more information on customizing the embed code, read Embedding Snippets.
