README.md
In treestats: Phylogenetic Tree Statistics

Treestats
Measuring properties of phylogenetic trees
The treestats R package contains rapid, C++ based, functions to
calculate summary statistics on phylogenies. For some functions (but not all, see below), the
phylogenies are required to be ultrametric and/or binary.
Getting started
Installation
To get started, you can either install from CRAN or use the latest
version from GitHub:
install.packages("treestats") # install from CRAN
# use the devtools package to install latest version from GitHub:
install.packages("devtools")
devtools::install_github("thijsjanzen/treestats")
Basic usage
Given a tree (for example a simulated tree, as in the code example), you
can either access individual statistics, or calculate all currently
implemented statistics:
focal_tree <- ape::rphylo(n = 10, birth = 1, death = 0)
colless_stat <- treestats::colless(focal_tree)
all_stats <- treestats::calc_all_stats(focal_tree)
List of statistics
The following summary statistics are included:
Statistic
Information
Normalization
Assumes Ultrametric tree
Requires binary tree
Reference
area_per_pair
Topology
Yule
NO
YES
Lima et al., 2020
average_leaf_depth
Topology
Yule
NO
YES
Shao & Sokal, 1990
avg_ladder
Topology
None
NO
YES
Kendall et al., 2018
avg_vert_depth
Topology
None
NO
NO
Herrada, 2011
b1
Topology
Tips
NO
NO
Shao & Sokal, 1990
b2
Topology
Yule
NO
NO
Shao & Sokal, 1990
beta
Topology
None
NO
YES
Aldous, 1996
blum
Topology
None
NO
YES
Blum & François, 2006
cherries
Topology
Yule
NO
YES
McKenzie et al., 1999
colless
Topology
Yule
NO
YES
Colless, 1982
colless_corr
Topology
None
NO
YES
Heard, 1992
colless_quad
Topology
None
NO
YES
Bartoszek et al., 2021
crown_age
Branching times
None
NO
NO
diameter
Topology
None
NO
YES
Chindelevitch et al., 2021
double_cherries
Topology
None
NO
YES
Chindelevitch et al., 2021
eigen_centrality
Topology
None
NO
NO
Chindelevitch et al., 2021
eigen_centralityW
Topology + branch lengths
None
NO
NO
Chindelevitch et al., 2021
ew_colless
Topology
None
NO
YES
Mooers & S. B. Heard, 1997
four_prong
Topology
None
NO
YES
Chindelevitch et al., 2021
gamma
Branching times
None
YES
NO
Pybus & Harvey, 2000
i_stat
Topology
None
NO
YES
Fusco & Cronk, 1995
il_number
Topology
Tips
NO
NO
Kendall et al., 2018
imbalance_steps
Topology
Tips
NO
NO
Janzen & Etienne, 2024
j_one
Topology
None
NO
YES
Lemant et al., 2022
j_stat
Topology + branch lengths
None
NO
NO
Izsák & Papp, 2000
laplace_spectrum_a
Topology + branch lengths
None
YES
NO
Lewitus & Morlon, 2016
laplace_spectrum_e
Topology + branch lengths
None
YES
NO
Lewitus & Morlon, 2016
laplace_spectrum_g
Topology + branch lengths
None
YES
NO
Lewitus & Morlon, 2016
laplace_spectrum_p
Topology + branch lengths
None
YES
NO
Lewitus & Morlon, 2016
max_adj
Topology + branch lengths
None
NO
YES
Chindelevitch et al., 2021
max_betweenness
Topology
Tips
NO
YES
Chindelevitch et al., 2021
max_closeness
Topology
Tips
NO
YES
Chindelevitch et al., 2021
max_closenessW
Topology + branch lengths
None
NO
YES
Chindelevitch et al., 2021
max_del_width
Topology
Tips
NO
NO
Colijn & Gardy, 2014
max_depth
Topology
Tips
NO
NO
Colijn & Gardy, 2014
max_ladder
Topology
None
NO
YES
Kendall et al., 2018
max_laplace
Topology + branch lengths
None
NO
YES
Chindelevitch et al., 2021
max_width
Topology
Tips
NO
NO
Colijn & Gardy, 2014
mean_branch_length
Topology + branch lengths
None
NO
NO
Janzen & Etienne, 2017
mean_branch_length_ext
Topology + branch lengths
None
NO
NO
Saulnier et al., 2017
mean_branch_length_int
Topology + branch lengths
None
NO
NO
Saulnier et al., 2017
min_adj
Topology + branch lengths
None
NO
YES
Chindelevitch et al., 2021
min_laplace
Topology + branch lengths
None
NO
YES
Chindelevitch et al., 2021
mntd
Topology + branch lengths
None
NO
NO
Webb et al., 2002
mpd
Topology + branch lengths
Tips
NO
NO
Webb et al., 2002
mw_over_md
Topology
None
NO
NO
Colijn & Gardy, 2014
nltt_base
Branching times
None
YES
NO
Janzen et al., 2015
number_of_lineages
Topology + branch lengths
None
NO
NO
phylogenetic_div
Topology + branch lengths
None
NO
NO
Faith, 1992
pigot_rho
Branching times
None
YES
NO
Pigot et al., 2010
pitchforks
Topology
Tips
NO
NO
Kendall et al., 2018
psv
Topology + branch lengths
Tips
NO
NO
Helmus et al., 2007
rogers
Topology
Tips
NO
YES
Rogers, 1996
root_imbalance
Topology
None
NO
YES
Guyer et al., 1993
rquartet
Topology
Yule
NO
NO
Coronado et al., 2019
sackin
Topology
Yule
NO
YES
Sackin, 1972
stairs
Topology
None
NO
YES
Norström et al., 2012
stairs2
Topology
None
NO
YES
Norström et al., 2012
symmetry_nodes
Topology
Tips
NO
YES
Kersting & Fischer, 2021
tot_coph
Topology
Yule
NO
YES
Mir et al., 2013
tot_internal_path
Topology
None
NO
NO
Knuth, 1997
tot_path
Topology
None
NO
YES
Colijn & Gardy, 2014
tree_height
Branching times
None
NO
NO
treeness
Topology + branch lengths
None
NO
NO
Astolfi & Zonta-Sgaramella, 1984
var_branch_length
Topology + branch lengths
None
NO
NO
Saulnier et al., 2017
var_branch_length_ext
Topology + branch lengths
None
NO
NO
Saulnier et al., 2017
var_branch_length_int
Topology + branch lengths
None
NO
NO
Saulnier et al., 2017
var_depth
Topology
Yule
NO
NO
Coronado et al., 2020
vpd
Topology + branch lengths
None
NO
NO
Webb et al., 2002
wiener
Topology + branch lengths
None
NO
YES
Chindelevitch et al., 2021
Rcpp
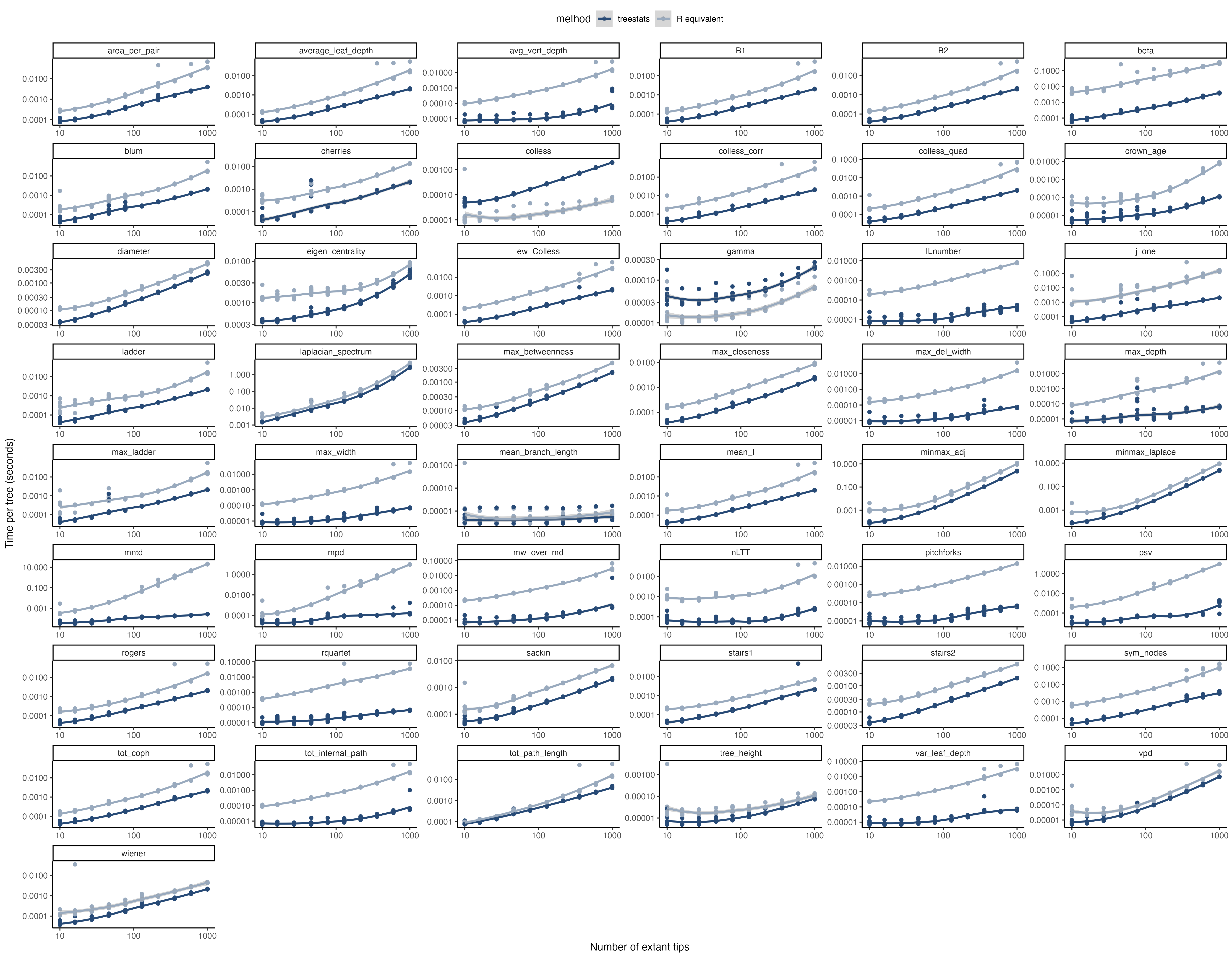
For all of these statistics, the package provides Rcpp versions that are
much, much faster than their R sister functions. Furthermore, some
additional functions have been improved as well:
ape::branching.times
DDD::phylo2L
* DDD::L2phylo
C++ Library
For the Rcpp improved summary statistics (excluding statistics that rely
on the calculation of eigen values, as these rely on the Rcpp
independent Eigen code), R independent C++ code is provided in the
inst/include folder. These can be independently linked by adding the
treestats package in the DESCRIPTION in both the LinkingTo and Depends
fields. Then, in your package, you can also calculate these functions.
Please note that for all functions, there are two versions available: 1)
based on input of a phylo object, which is typically one 2-column matrix
containing all edges, and a vector containing the edge lengths
(depending on which information is required to calculate the statistic).
2) based on input of an Ltable (Lineage table), which is a 4-column
matrix containing information on each species, being 1) birth time, 2)
parent species, 3) species label and 4) death time (or -1 if extant).
Ltable input can be useful when summary statistics are required for more
complicated simulation models.
Try the treestats package in your browser
Any scripts or data that you put into this service are public.
treestats documentation built on Sept. 14, 2024, 9:08 a.m.

Treestats
Measuring properties of phylogenetic trees
The treestats R package contains rapid, C++ based, functions to calculate summary statistics on phylogenies. For some functions (but not all, see below), the phylogenies are required to be ultrametric and/or binary.
Getting started
Installation
To get started, you can either install from CRAN or use the latest version from GitHub:
install.packages("treestats") # install from CRAN
# use the devtools package to install latest version from GitHub:
install.packages("devtools")
devtools::install_github("thijsjanzen/treestats")
Basic usage
Given a tree (for example a simulated tree, as in the code example), you can either access individual statistics, or calculate all currently implemented statistics:
focal_tree <- ape::rphylo(n = 10, birth = 1, death = 0)
colless_stat <- treestats::colless(focal_tree)
all_stats <- treestats::calc_all_stats(focal_tree)
List of statistics
The following summary statistics are included:
Statistic Information Normalization Assumes Ultrametric tree Requires binary tree Reference area_per_pair Topology Yule NO YES Lima et al., 2020 average_leaf_depth Topology Yule NO YES Shao & Sokal, 1990 avg_ladder Topology None NO YES Kendall et al., 2018 avg_vert_depth Topology None NO NO Herrada, 2011 b1 Topology Tips NO NO Shao & Sokal, 1990 b2 Topology Yule NO NO Shao & Sokal, 1990 beta Topology None NO YES Aldous, 1996 blum Topology None NO YES Blum & François, 2006 cherries Topology Yule NO YES McKenzie et al., 1999 colless Topology Yule NO YES Colless, 1982 colless_corr Topology None NO YES Heard, 1992 colless_quad Topology None NO YES Bartoszek et al., 2021 crown_age Branching times None NO NO diameter Topology None NO YES Chindelevitch et al., 2021 double_cherries Topology None NO YES Chindelevitch et al., 2021 eigen_centrality Topology None NO NO Chindelevitch et al., 2021 eigen_centralityW Topology + branch lengths None NO NO Chindelevitch et al., 2021 ew_colless Topology None NO YES Mooers & S. B. Heard, 1997 four_prong Topology None NO YES Chindelevitch et al., 2021 gamma Branching times None YES NO Pybus & Harvey, 2000 i_stat Topology None NO YES Fusco & Cronk, 1995 il_number Topology Tips NO NO Kendall et al., 2018 imbalance_steps Topology Tips NO NO Janzen & Etienne, 2024 j_one Topology None NO YES Lemant et al., 2022 j_stat Topology + branch lengths None NO NO Izsák & Papp, 2000 laplace_spectrum_a Topology + branch lengths None YES NO Lewitus & Morlon, 2016 laplace_spectrum_e Topology + branch lengths None YES NO Lewitus & Morlon, 2016 laplace_spectrum_g Topology + branch lengths None YES NO Lewitus & Morlon, 2016 laplace_spectrum_p Topology + branch lengths None YES NO Lewitus & Morlon, 2016 max_adj Topology + branch lengths None NO YES Chindelevitch et al., 2021 max_betweenness Topology Tips NO YES Chindelevitch et al., 2021 max_closeness Topology Tips NO YES Chindelevitch et al., 2021 max_closenessW Topology + branch lengths None NO YES Chindelevitch et al., 2021 max_del_width Topology Tips NO NO Colijn & Gardy, 2014 max_depth Topology Tips NO NO Colijn & Gardy, 2014 max_ladder Topology None NO YES Kendall et al., 2018 max_laplace Topology + branch lengths None NO YES Chindelevitch et al., 2021 max_width Topology Tips NO NO Colijn & Gardy, 2014 mean_branch_length Topology + branch lengths None NO NO Janzen & Etienne, 2017 mean_branch_length_ext Topology + branch lengths None NO NO Saulnier et al., 2017 mean_branch_length_int Topology + branch lengths None NO NO Saulnier et al., 2017 min_adj Topology + branch lengths None NO YES Chindelevitch et al., 2021 min_laplace Topology + branch lengths None NO YES Chindelevitch et al., 2021 mntd Topology + branch lengths None NO NO Webb et al., 2002 mpd Topology + branch lengths Tips NO NO Webb et al., 2002 mw_over_md Topology None NO NO Colijn & Gardy, 2014 nltt_base Branching times None YES NO Janzen et al., 2015 number_of_lineages Topology + branch lengths None NO NO phylogenetic_div Topology + branch lengths None NO NO Faith, 1992 pigot_rho Branching times None YES NO Pigot et al., 2010 pitchforks Topology Tips NO NO Kendall et al., 2018 psv Topology + branch lengths Tips NO NO Helmus et al., 2007 rogers Topology Tips NO YES Rogers, 1996 root_imbalance Topology None NO YES Guyer et al., 1993 rquartet Topology Yule NO NO Coronado et al., 2019 sackin Topology Yule NO YES Sackin, 1972 stairs Topology None NO YES Norström et al., 2012 stairs2 Topology None NO YES Norström et al., 2012 symmetry_nodes Topology Tips NO YES Kersting & Fischer, 2021 tot_coph Topology Yule NO YES Mir et al., 2013 tot_internal_path Topology None NO NO Knuth, 1997 tot_path Topology None NO YES Colijn & Gardy, 2014 tree_height Branching times None NO NO treeness Topology + branch lengths None NO NO Astolfi & Zonta-Sgaramella, 1984 var_branch_length Topology + branch lengths None NO NO Saulnier et al., 2017 var_branch_length_ext Topology + branch lengths None NO NO Saulnier et al., 2017 var_branch_length_int Topology + branch lengths None NO NO Saulnier et al., 2017 var_depth Topology Yule NO NO Coronado et al., 2020 vpd Topology + branch lengths None NO NO Webb et al., 2002 wiener Topology + branch lengths None NO YES Chindelevitch et al., 2021Rcpp
For all of these statistics, the package provides Rcpp versions that are much, much faster than their R sister functions. Furthermore, some additional functions have been improved as well: ape::branching.times DDD::phylo2L * DDD::L2phylo

C++ Library
For the Rcpp improved summary statistics (excluding statistics that rely on the calculation of eigen values, as these rely on the Rcpp independent Eigen code), R independent C++ code is provided in the inst/include folder. These can be independently linked by adding the treestats package in the DESCRIPTION in both the LinkingTo and Depends fields. Then, in your package, you can also calculate these functions.
Please note that for all functions, there are two versions available: 1) based on input of a phylo object, which is typically one 2-column matrix containing all edges, and a vector containing the edge lengths (depending on which information is required to calculate the statistic). 2) based on input of an Ltable (Lineage table), which is a 4-column matrix containing information on each species, being 1) birth time, 2) parent species, 3) species label and 4) death time (or -1 if extant).
Ltable input can be useful when summary statistics are required for more complicated simulation models.
Try the treestats package in your browser
Any scripts or data that you put into this service are public.
Add the following code to your website.
For more information on customizing the embed code, read Embedding Snippets.
