In shbrief/GenomicSuperSignature: Interpretation of RNA-seq experiments through robust, efficient comparison to public databases
knitr::opts_chunk$set(
collapse = TRUE, comment = "#>"
)
Citing GenomicSuperSignature
Please cite GenomicSuperSignature as follows:
Oh, S., Geistlinger, L., Ramos, M. et al. GenomicSuperSignature facilitates interpretation of RNA-seq experiments through robust, efficient comparison to public databases. Nat Commun 13, 3695 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-31411-3
Setup
Install and load package
if (!require("BiocManager"))
install.packages("BiocManager")
BiocManager::install("GenomicSuperSignature")
library(GenomicSuperSignature)
Download RAVmodel
You can download GenomicSuperSignature from Google Cloud bucket using
GenomicSuperSignature::getModel function. Currently available models are
built from top 20 PCs of 536 studies (containing 44,890 samples) containing
13,934 common genes from each of 536 study's top 90% varying genes based on
their study-level standard deviation. There are two versions of this RAVmodel
annotated with different gene sets for GSEA: MSigDB C2 (C2) and three
priors from PLIER package (PLIERpriors). In this vignette, we are showing
the C2 annotated model.
Note that the first interactive run of this code, you will be asked to allow
R to create a cache directory. The model file will be stored there and
subsequent calls to getModel will read from the cache.
RAVmodel <- getModel("C2", load=TRUE)
Content of RAVmodel
RAVindex is a matrix containing genes in rows and RAVs in columns. colData
slot provides the information on each RAVs, such as GSEA annotation and
studies involved in each cluster. metadata slot stores model construction
information. trainingData slot contains the information on individual
studies in training dataset, such as MeSH terms assigned to each study.
RAVmodel
version(RAVmodel)
geneSets(RAVmodel)
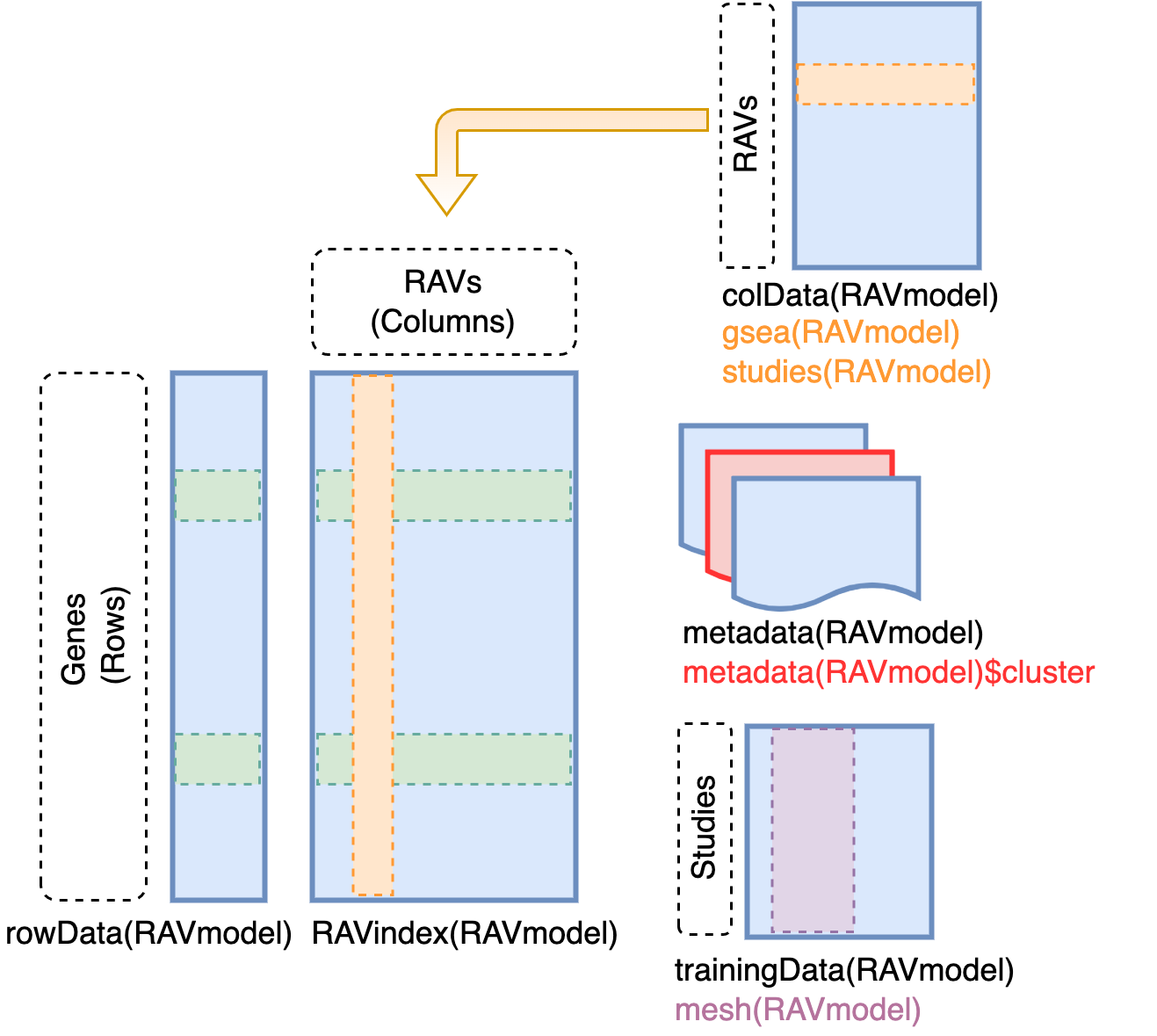
RAVindex
Replicable Axis of Variation (RAV) index is the main component of
GenomicSuperSignature. It serves as an index connecting new datasets and the
existing database. You can access it through GenomicSuperSignature::RAVindex
(equivalent of SummarizedExperiment::assay). Rows are genes and columns are
RAVs.
Here, RAVmodel consists of 13,934 genes and 4,764 RAVs.
class(RAVindex(RAVmodel))
dim(RAVindex(RAVmodel))
RAVindex(RAVmodel)[1:4, 1:4]
Metadata for RAVmodel
Metadata slot of RAVmodel contains information related to the model building.
names(metadata(RAVmodel))
cluster : cluster membership of each PCs from the training dataset size : an integer vector with the length of clusters, containing the number
of PCs in each cluster k : the number of all clusters in the given RAVmodel n : the number of top PCs kept from each study in the training datasetgeneSets : the name of gene sets used for GSEA annotation MeSH_freq : the frequency of MeSH terms associated with the training
dataset. MeSH terms like 'Humans' and 'RNA-seq' are top ranked (which is very
expected) because the training dataset of this model is Human RNA sequencing
data. updateNote : a brief note on the given model's specificationversion : the version of the given model
head(metadata(RAVmodel)$cluster)
head(metadata(RAVmodel)$size)
metadata(RAVmodel)$k
metadata(RAVmodel)$n
geneSets(RAVmodel)
head(metadata(RAVmodel)$MeSH_freq)
updateNote(RAVmodel)
metadata(RAVmodel)$version
Studies in each RAV
You can find which studies are in each cluster using studies method. Output is
a list with the length of clusters, where each element is a character vector
containing the name of studies in each cluster.
length(studies(RAVmodel))
studies(RAVmodel)[1:3]
You can check which PC from different studies are in RAVs using PCinRAV.
PCinRAV(RAVmodel, 2)
Silhouette width for each RAV
Silhouette width ranges from -1 to 1 for each cluster. Typically, it is
interpreted as follows:
- Values close to 1 suggest that the observation is well matched to the
assigned cluster
- Values close to 0 suggest that the observation is borderline matched
between two clusters
- Values close to -1 suggest that the observations may be assigned to the
wrong cluster
For RAVmodel, the average silhouette width of each cluster is a quality control
measure and suggested as a secondary reference to choose proper RAVs,
following validation score.
x <- silhouetteWidth(RAVmodel)
head(x) # average silhouette width of the first 6 RAVs
GSEA on each RAV
Pre-processed GSEA results on each RAV are stored in RAVmodel and can be
accessed through gsea function.
class(gsea(RAVmodel))
class(gsea(RAVmodel)[[1]])
length(gsea(RAVmodel))
gsea(RAVmodel)[1]
MeSH terms for each study
You can find MeSH terms associated with each study using mesh method.
Output is a list with the length of studies used for training. Each element of
this output list is a data frame containing the assigned MeSH terms and the
detail of them. The last column bagOfWords is the frequency of the MeSH term
in the whole training dataset.
length(mesh(RAVmodel))
mesh(RAVmodel)[1]
PCA summary for each study
PCA summary of each study can be accessed through PCAsummary method. Output
is a list with the length of studies, where each element is a matrix containing
PCA summary results: standard deviation (SD), variance explained by each PC
(Variance), and the cumulative variance explained (Cumulative).
length(PCAsummary(RAVmodel))
PCAsummary(RAVmodel)[1]
Other relevant code
The workflow to build the RAVmodel is available from https://github.com/shbrief/model_building which is archived in Zenodo with the identifier https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6496552. All analyses presented in the GenomicSuperSignatures manuscript are reproducible using code accessible from https://github.com/shbrief/GenomicSuperSignaturePaper/ and archived in Zenodo with the identifier [https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6496612].
Session Info
sessionInfo()
shbrief/GenomicSuperSignature documentation built on May 3, 2023, 10:07 p.m.
knitr::opts_chunk$set( collapse = TRUE, comment = "#>" )
Citing GenomicSuperSignature
Please cite GenomicSuperSignature as follows:
Oh, S., Geistlinger, L., Ramos, M. et al. GenomicSuperSignature facilitates interpretation of RNA-seq experiments through robust, efficient comparison to public databases. Nat Commun 13, 3695 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-022-31411-3
Setup
Install and load package
if (!require("BiocManager")) install.packages("BiocManager") BiocManager::install("GenomicSuperSignature")
library(GenomicSuperSignature)
Download RAVmodel
You can download GenomicSuperSignature from Google Cloud bucket using
GenomicSuperSignature::getModel function. Currently available models are
built from top 20 PCs of 536 studies (containing 44,890 samples) containing
13,934 common genes from each of 536 study's top 90% varying genes based on
their study-level standard deviation. There are two versions of this RAVmodel
annotated with different gene sets for GSEA: MSigDB C2 (C2) and three
priors from PLIER package (PLIERpriors). In this vignette, we are showing
the C2 annotated model.
Note that the first interactive run of this code, you will be asked to allow
R to create a cache directory. The model file will be stored there and
subsequent calls to getModel will read from the cache.
RAVmodel <- getModel("C2", load=TRUE)
Content of RAVmodel
RAVindex is a matrix containing genes in rows and RAVs in columns. colData
slot provides the information on each RAVs, such as GSEA annotation and
studies involved in each cluster. metadata slot stores model construction
information. trainingData slot contains the information on individual
studies in training dataset, such as MeSH terms assigned to each study.
RAVmodel version(RAVmodel) geneSets(RAVmodel)

RAVindex
Replicable Axis of Variation (RAV) index is the main component of
GenomicSuperSignature. It serves as an index connecting new datasets and the
existing database. You can access it through GenomicSuperSignature::RAVindex
(equivalent of SummarizedExperiment::assay). Rows are genes and columns are
RAVs.
Here, RAVmodel consists of 13,934 genes and 4,764 RAVs.
class(RAVindex(RAVmodel)) dim(RAVindex(RAVmodel)) RAVindex(RAVmodel)[1:4, 1:4]
Metadata for RAVmodel
Metadata slot of RAVmodel contains information related to the model building.
names(metadata(RAVmodel))
cluster: cluster membership of each PCs from the training datasetsize: an integer vector with the length of clusters, containing the number of PCs in each clusterk: the number of all clusters in the given RAVmodeln: the number of top PCs kept from each study in the training datasetgeneSets: the name of gene sets used for GSEA annotationMeSH_freq: the frequency of MeSH terms associated with the training dataset. MeSH terms like 'Humans' and 'RNA-seq' are top ranked (which is very expected) because the training dataset of this model is Human RNA sequencing data.updateNote: a brief note on the given model's specificationversion: the version of the given model
head(metadata(RAVmodel)$cluster) head(metadata(RAVmodel)$size) metadata(RAVmodel)$k metadata(RAVmodel)$n geneSets(RAVmodel) head(metadata(RAVmodel)$MeSH_freq) updateNote(RAVmodel) metadata(RAVmodel)$version
Studies in each RAV
You can find which studies are in each cluster using studies method. Output is
a list with the length of clusters, where each element is a character vector
containing the name of studies in each cluster.
length(studies(RAVmodel)) studies(RAVmodel)[1:3]
You can check which PC from different studies are in RAVs using PCinRAV.
PCinRAV(RAVmodel, 2)
Silhouette width for each RAV
Silhouette width ranges from -1 to 1 for each cluster. Typically, it is
interpreted as follows:
- Values close to 1 suggest that the observation is well matched to the
assigned cluster
- Values close to 0 suggest that the observation is borderline matched
between two clusters
- Values close to -1 suggest that the observations may be assigned to the
wrong cluster
For RAVmodel, the average silhouette width of each cluster is a quality control measure and suggested as a secondary reference to choose proper RAVs, following validation score.
x <- silhouetteWidth(RAVmodel) head(x) # average silhouette width of the first 6 RAVs
GSEA on each RAV
Pre-processed GSEA results on each RAV are stored in RAVmodel and can be
accessed through gsea function.
class(gsea(RAVmodel)) class(gsea(RAVmodel)[[1]]) length(gsea(RAVmodel)) gsea(RAVmodel)[1]
MeSH terms for each study
You can find MeSH terms associated with each study using mesh method.
Output is a list with the length of studies used for training. Each element of
this output list is a data frame containing the assigned MeSH terms and the
detail of them. The last column bagOfWords is the frequency of the MeSH term
in the whole training dataset.
length(mesh(RAVmodel)) mesh(RAVmodel)[1]
PCA summary for each study
PCA summary of each study can be accessed through PCAsummary method. Output
is a list with the length of studies, where each element is a matrix containing
PCA summary results: standard deviation (SD), variance explained by each PC
(Variance), and the cumulative variance explained (Cumulative).
length(PCAsummary(RAVmodel)) PCAsummary(RAVmodel)[1]
Other relevant code
The workflow to build the RAVmodel is available from https://github.com/shbrief/model_building which is archived in Zenodo with the identifier https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6496552. All analyses presented in the GenomicSuperSignatures manuscript are reproducible using code accessible from https://github.com/shbrief/GenomicSuperSignaturePaper/ and archived in Zenodo with the identifier [https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.6496612].
Session Info
sessionInfo()
Add the following code to your website.
For more information on customizing the embed code, read Embedding Snippets.
