cols_merge_range: Merge two columns to a value range column
In gt: Easily Create Presentation-Ready Display Tables
cols_merge_range R Documentation
Merge two columns to a value range column
Description
cols_merge_range() is a specialized variant of cols_merge(). It operates
by taking a two columns that constitute a range of values (col_begin and
col_end) and merges them into a single column. What results is a column
containing both values separated by an em dash. The column specified in
col_end is dropped from the output table.
Usage
cols_merge_range(
data,
col_begin,
col_end,
rows = everything(),
autohide = TRUE,
sep = NULL,
locale = NULL
)
Arguments
data
The gt table or gt group data object
obj:<gt_tbl> // required
This is the gt table object that is commonly created through use of the
gt() function.
OR
obj:<gt_group> // required
This is the gt group object that is commonly created through use of the
gt_group() function.
col_begin
Column to target for beginning of range
<column-targeting expression> // required
The column that contains values for the start of the range. While select
helper functions such as starts_with() and ends_with() can be used for
column targeting, it's recommended that a single column name be used. This
is to ensure that exactly one column is provided here.
col_end
Column to target for end of range
<column-targeting expression> // required
The column that contains values for the end of the range. While select
helper functions such as starts_with() and ends_with() can be used for
column targeting, it's recommended that a single column name be used. This
is to ensure that exactly one column is provided here.
rows
Rows to target
<row-targeting expression> // default: everything()
In conjunction with columns, we can specify which of their rows should
participate in the merging process. The default everything() results in
all rows in columns being formatted. Alternatively, we can supply a
vector of row IDs within c(), a vector of row indices, or a select
helper function (e.g. starts_with(), ends_with(), contains(),
matches(), num_range(), and everything()). We can also use
expressions to filter down to the rows we need
(e.g., [colname_1] > 100 & [colname_2] < 50).
autohide
Automatic hiding of the col_end column
scalar<logical> // default: TRUE
An option to automatically hide the column specified as
col_end. Any columns with their state changed to hidden will behave
the same as before, they just won't be displayed in the finalized table.
sep
Separator text for ranges
scalar<character> // default: NULL (optional)
The separator text that indicates the values are ranged. If a sep value
is not provided then the range separator specific to the locale provided
will be used (if a locale isn't specified then an en dash will be used).
You can specify the use of an en dash with "--"; a triple-hyphen sequence
("---") will be transformed to an em dash. Should you want hyphens to be
taken literally, the sep value can be supplied within the base I()
function.
locale
Locale identifier
scalar<character> // default: NULL (optional)
An optional locale identifier that can be used for applying a sep pattern
specific to a locale's rules. Examples include "en" for English (United
States) and "fr" for French (France). We can call info_locales() as a
useful reference for all of the locales that are supported. A locale ID can
be also set in the initial gt() function call (where it would be used
automatically by any function with a locale argument) but a locale
value provided here will override that global locale.
Value
An object of class gt_tbl.
Comparison with other column-merging functions
This function could be somewhat replicated using cols_merge(), however,
cols_merge_range() employs the following specialized operations for NA
handling:
-
NAs in col_begin (but not col_end) result in a display of only
-
NAs in col_end (but not col_begin) result in a display of only
the col_begin values only for the merged column (this is the converse of
the previous)
-
NAs both in col_begin and col_end result in missing values for
the merged column
Any resulting NA values in the col_begin column following the merge
operation can be easily formatted using sub_missing(). Separate calls of
sub_missing() can be used for the col_begin and col_end columns for
finer control of the replacement values.
This function is part of a set of four column-merging functions. The other
three are the general cols_merge() function and the specialized
cols_merge_uncert() and cols_merge_n_pct() functions. These functions
operate similarly, where the non-target columns can be optionally hidden from
the output table through the hide_columns or autohide options.
Examples
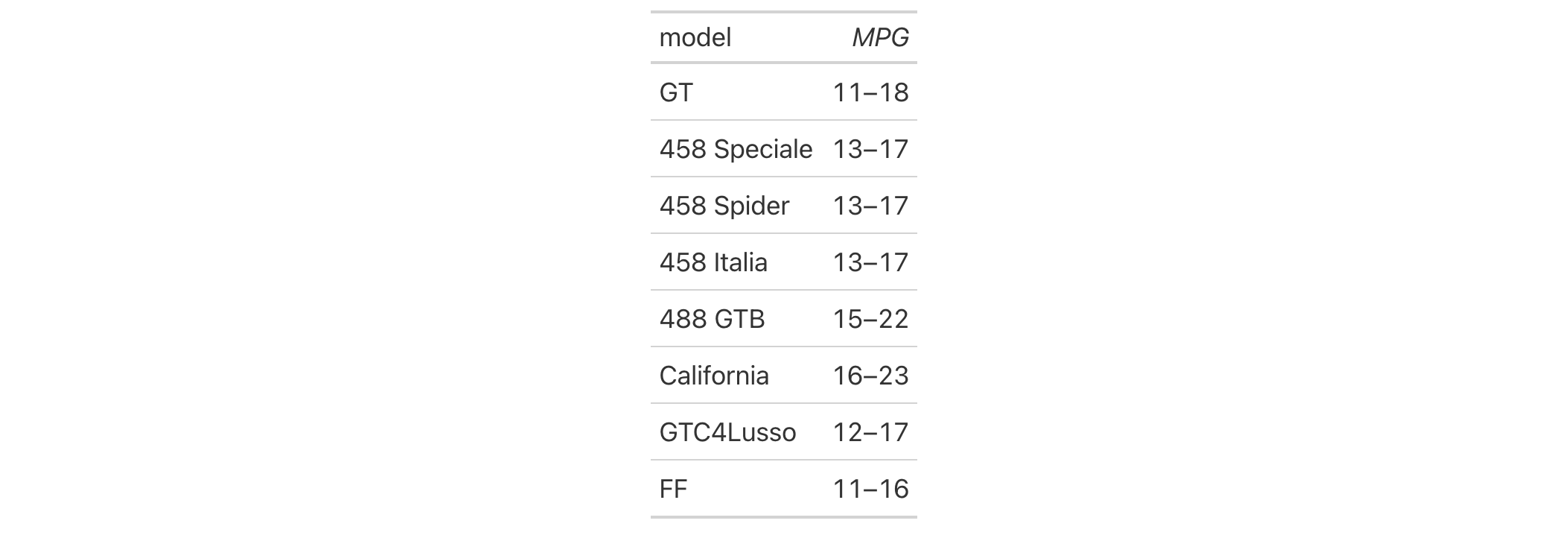
Let's use a subset of the gtcars dataset to create a gt table,
keeping only the model, mpg_c, and mpg_h columns. Merge the "mpg*"
columns together as a single range column (which is labeled as MPG, in
italics) using the cols_merge_range() function. After the merging process,
the column label for the mpg_c column is updated with cols_label() to
better describe the content.
gtcars |>
dplyr::select(model, starts_with("mpg")) |>
dplyr::slice(1:8) |>
gt() |>
cols_merge_range(
col_begin = mpg_c,
col_end = mpg_h
) |>
cols_label(mpg_c = md("*MPG*"))
Function ID
5-16
Function Introduced
v0.2.0.5 (March 31, 2020)
See Also
Other column modification functions:
cols_add(),
cols_align(),
cols_align_decimal(),
cols_hide(),
cols_label(),
cols_label_with(),
cols_merge(),
cols_merge_n_pct(),
cols_merge_uncert(),
cols_move(),
cols_move_to_end(),
cols_move_to_start(),
cols_nanoplot(),
cols_unhide(),
cols_units(),
cols_width()
gt documentation built on Jan. 22, 2026, 9:07 a.m.
| cols_merge_range | R Documentation |
Merge two columns to a value range column
Description
cols_merge_range() is a specialized variant of cols_merge(). It operates
by taking a two columns that constitute a range of values (col_begin and
col_end) and merges them into a single column. What results is a column
containing both values separated by an em dash. The column specified in
col_end is dropped from the output table.
Usage
cols_merge_range(
data,
col_begin,
col_end,
rows = everything(),
autohide = TRUE,
sep = NULL,
locale = NULL
)
Arguments
data |
The gt table or gt group data object
This is the gt table object that is commonly created through use of the
OR
This is the gt group object that is commonly created through use of the
|
col_begin |
Column to target for beginning of range
The column that contains values for the start of the range. While select
helper functions such as |
col_end |
Column to target for end of range
The column that contains values for the end of the range. While select
helper functions such as |
rows |
Rows to target
In conjunction with |
autohide |
Automatic hiding of the
An option to automatically hide the column specified as
|
sep |
Separator text for ranges
The separator text that indicates the values are ranged. If a |
locale |
Locale identifier
An optional locale identifier that can be used for applying a |
Value
An object of class gt_tbl.
Comparison with other column-merging functions
This function could be somewhat replicated using cols_merge(), however,
cols_merge_range() employs the following specialized operations for NA
handling:
-
NAs incol_begin(but notcol_end) result in a display of only -
NAs incol_end(but notcol_begin) result in a display of only thecol_beginvalues only for the merged column (this is the converse of the previous) -
NAs both incol_beginandcol_endresult in missing values for the merged column
Any resulting NA values in the col_begin column following the merge
operation can be easily formatted using sub_missing(). Separate calls of
sub_missing() can be used for the col_begin and col_end columns for
finer control of the replacement values.
This function is part of a set of four column-merging functions. The other
three are the general cols_merge() function and the specialized
cols_merge_uncert() and cols_merge_n_pct() functions. These functions
operate similarly, where the non-target columns can be optionally hidden from
the output table through the hide_columns or autohide options.
Examples
Let's use a subset of the gtcars dataset to create a gt table,
keeping only the model, mpg_c, and mpg_h columns. Merge the "mpg*"
columns together as a single range column (which is labeled as MPG, in
italics) using the cols_merge_range() function. After the merging process,
the column label for the mpg_c column is updated with cols_label() to
better describe the content.
gtcars |>
dplyr::select(model, starts_with("mpg")) |>
dplyr::slice(1:8) |>
gt() |>
cols_merge_range(
col_begin = mpg_c,
col_end = mpg_h
) |>
cols_label(mpg_c = md("*MPG*"))

Function ID
5-16
Function Introduced
v0.2.0.5 (March 31, 2020)
See Also
Other column modification functions:
cols_add(),
cols_align(),
cols_align_decimal(),
cols_hide(),
cols_label(),
cols_label_with(),
cols_merge(),
cols_merge_n_pct(),
cols_merge_uncert(),
cols_move(),
cols_move_to_end(),
cols_move_to_start(),
cols_nanoplot(),
cols_unhide(),
cols_units(),
cols_width()
Add the following code to your website.
For more information on customizing the embed code, read Embedding Snippets.
