fmt: Set a column format with a formatter function
In rstudio/gt: Easily Create Presentation-Ready Display Tables
fmt R Documentation
Set a column format with a formatter function
Description
fmt() provides a way to execute custom formatting functionality with raw
data values in a way that can consider all output contexts.
Along with the columns and rows arguments that provide some precision in
targeting data cells, the fns argument allows you to define one or more
functions for manipulating the raw data.
If providing a single function to fns, the recommended format is in the
form: fns = function(x) .... This single function will format the targeted
data cells the same way regardless of the output format (e.g., HTML, LaTeX,
RTF).
If you require formatting of x that depends on the output format, a list of
functions can be provided for the html, latex, rtf, and default
contexts. This can be in the form of fns = list(html = function(x) ..., latex = function(x) ..., default = function(x) ...). In this
multiple-function case, we recommended including the default function as a
fallback if all contexts aren't provided.
Usage
fmt(data, columns = everything(), rows = everything(), compat = NULL, fns)
Arguments
data
The gt table data object
obj:<gt_tbl> // required
This is the gt table object that is commonly created through use of the
gt() function.
columns
Columns to target
<column-targeting expression> // default: everything()
Can either be a series of column names provided in c(), a vector of
column indices, or a select helper function (e.g. starts_with(),
ends_with(), contains(), matches(), num_range() and everything()).
rows
Rows to target
<row-targeting expression> // default: everything()
In conjunction with columns, we can specify which of their rows should
undergo formatting. The default everything() results in all rows in
columns being formatted. Alternatively, we can supply a vector of row
captions within c(), a vector of row indices, or a select helper
function (e.g. starts_with(), ends_with(), contains(), matches(),
num_range(), and everything()). We can also use expressions to filter
down to the rows we need (e.g., [colname_1] > 100 & [colname_2] < 50).
compat
Formatting compatibility
vector<character> // default: NULL (optional)
An optional vector that provides the compatible classes for the formatting.
By default this is NULL.
fns
Formatting functions
function|list of functions // required
Either a single formatting function or a named list of functions. Can also
be anonymous functions, in both base R (\(x) x + 1) and rlang
(~.x + 1) syntax.
Value
An object of class gt_tbl.
Examples
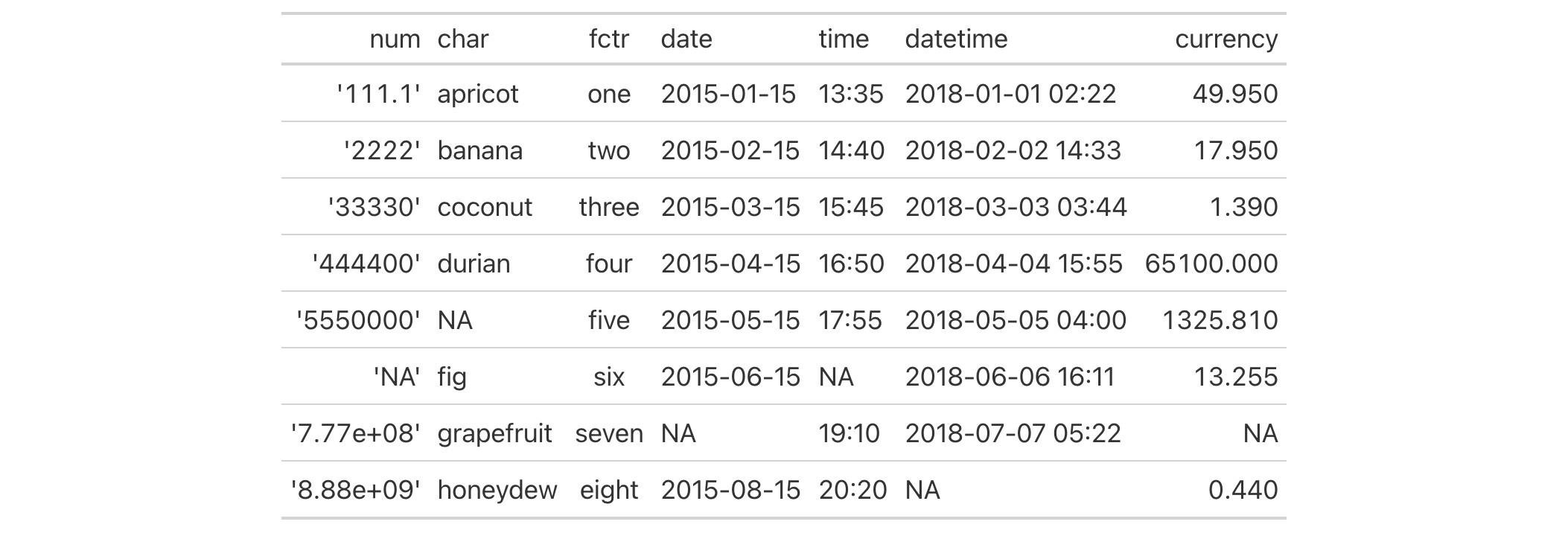
Use the exibble dataset to create a gt table. We'll format the
numeric values in the num column with fmt(). We supply a functions to
the fns argument. This supplied function will take values in the
column (x), multiply them by 1000, and exclose them in single quotes.
exibble |>
dplyr::select(-row, -group) |>
gt() |>
fmt(
columns = num,
fns = function(x) {
paste0("'", x * 1000, "'")
}
)
Function ID
3-30
Function Introduced
v0.2.0.5 (March 31, 2020)
See Also
Other data formatting functions:
data_color(),
fmt_auto(),
fmt_bins(),
fmt_bytes(),
fmt_chem(),
fmt_country(),
fmt_currency(),
fmt_date(),
fmt_datetime(),
fmt_duration(),
fmt_email(),
fmt_engineering(),
fmt_flag(),
fmt_fraction(),
fmt_icon(),
fmt_image(),
fmt_index(),
fmt_integer(),
fmt_markdown(),
fmt_number(),
fmt_partsper(),
fmt_passthrough(),
fmt_percent(),
fmt_roman(),
fmt_scientific(),
fmt_spelled_num(),
fmt_tf(),
fmt_time(),
fmt_units(),
fmt_url(),
sub_large_vals(),
sub_missing(),
sub_small_vals(),
sub_values(),
sub_zero()
rstudio/gt documentation built on March 29, 2025, 4:02 a.m.
| fmt | R Documentation |
Set a column format with a formatter function
Description
fmt() provides a way to execute custom formatting functionality with raw
data values in a way that can consider all output contexts.
Along with the columns and rows arguments that provide some precision in
targeting data cells, the fns argument allows you to define one or more
functions for manipulating the raw data.
If providing a single function to fns, the recommended format is in the
form: fns = function(x) .... This single function will format the targeted
data cells the same way regardless of the output format (e.g., HTML, LaTeX,
RTF).
If you require formatting of x that depends on the output format, a list of
functions can be provided for the html, latex, rtf, and default
contexts. This can be in the form of fns = list(html = function(x) ..., latex = function(x) ..., default = function(x) ...). In this
multiple-function case, we recommended including the default function as a
fallback if all contexts aren't provided.
Usage
fmt(data, columns = everything(), rows = everything(), compat = NULL, fns)
Arguments
data |
The gt table data object
This is the gt table object that is commonly created through use of the
|
columns |
Columns to target
Can either be a series of column names provided in |
rows |
Rows to target
In conjunction with |
compat |
Formatting compatibility
An optional vector that provides the compatible classes for the formatting.
By default this is |
fns |
Formatting functions
Either a single formatting function or a named list of functions. Can also
be anonymous functions, in both base R ( |
Value
An object of class gt_tbl.
Examples
Use the exibble dataset to create a gt table. We'll format the
numeric values in the num column with fmt(). We supply a functions to
the fns argument. This supplied function will take values in the
column (x), multiply them by 1000, and exclose them in single quotes.
exibble |>
dplyr::select(-row, -group) |>
gt() |>
fmt(
columns = num,
fns = function(x) {
paste0("'", x * 1000, "'")
}
)

Function ID
3-30
Function Introduced
v0.2.0.5 (March 31, 2020)
See Also
Other data formatting functions:
data_color(),
fmt_auto(),
fmt_bins(),
fmt_bytes(),
fmt_chem(),
fmt_country(),
fmt_currency(),
fmt_date(),
fmt_datetime(),
fmt_duration(),
fmt_email(),
fmt_engineering(),
fmt_flag(),
fmt_fraction(),
fmt_icon(),
fmt_image(),
fmt_index(),
fmt_integer(),
fmt_markdown(),
fmt_number(),
fmt_partsper(),
fmt_passthrough(),
fmt_percent(),
fmt_roman(),
fmt_scientific(),
fmt_spelled_num(),
fmt_tf(),
fmt_time(),
fmt_units(),
fmt_url(),
sub_large_vals(),
sub_missing(),
sub_small_vals(),
sub_values(),
sub_zero()
Add the following code to your website.
For more information on customizing the embed code, read Embedding Snippets.
