from_column: Reference a column of values for certain parameters
In rstudio/gt: Easily Create Presentation-Ready Display Tables
from_column R Documentation
Reference a column of values for certain parameters
Description
It can be useful to obtain parameter values from a column in a
gt for functions that operate on the table body and stub cells. For
example, you might want to indent row labels in the stub. You could call
tab_stub_indent() and indent different rows to various indentation levels.
However, each level of indentation applied necessitates a new call of that
function. To make this better, we can use indentation values available in a
table column via the from_column() helper function. For the
tab_stub_indent() case, you'd invoke this helper at the indent argument
and specify the column that has the values.
Usage
from_column(column, na_value = NULL, fn = NULL)
Arguments
column
Column name
scalar<character> // required
A single column name in quotation marks. Values will be extracted from this
column and provided to compatible arguments.
na_value
Default replacement for NA values
scalar<character|numeric|logical> // default: NULL (optional)
A single value to replace any NA values in the column. Take care to
provide a value that is of the same type as the column values to avoid
any undesirable coercion.
fn
Function to apply
function|formula // default: NULL (optional)
If a function is provided here, any values extracted from the table
column (except NA values) can be mutated.
Value
A list object of class gt_column.
Functions that allow the use of the from_column() helper
Only certain functions (and furthermore a subset of arguments within each)
support the use of from_column() for accessing varying parameter values.
These functions are:
-
tab_stub_indent()
-
fmt_number()
-
fmt_integer()
-
fmt_scientific()
-
fmt_engineering()
-
fmt_percent()
-
fmt_partsper()
-
fmt_fraction()
-
fmt_currency()
-
fmt_roman()
-
fmt_index()
-
fmt_spelled_num()
-
fmt_bytes()
-
fmt_date()
-
fmt_time()
-
fmt_datetime()
-
fmt_url()
-
fmt_image()
-
fmt_flag()
-
fmt_markdown()
-
fmt_passthrough()
Within help documents for each of these functions you'll find the
Compatibility of arguments with the from_column() helper function section
and sections like these describe which arguments support the use of
from_column().
Examples
from_column() can be used in a variety of formatting functions so that
values for common options don't have to be static, they can change in every
row (so long as you have a column of compatible option values). Here's an
example where we have a table of repeating numeric values along with a column
of currency codes. We can format the numbers to currencies with
fmt_currency() and use from_column() to reference the column of currency
codes, giving us values that are each formatted as having a different
currency.
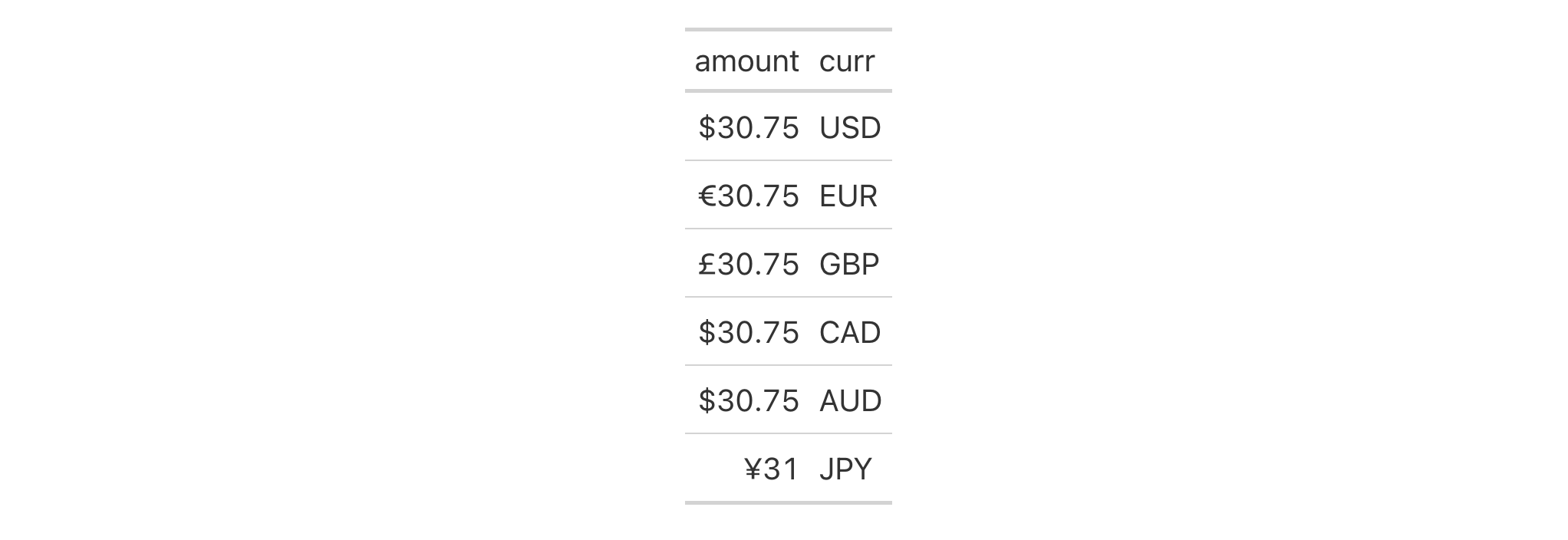
dplyr::tibble(
amount = rep(30.75, 6),
curr = c("USD", "EUR", "GBP", "CAD", "AUD", "JPY"),
) |>
gt() |>
fmt_currency(currency = from_column(column = "curr"))
Let's summarize the gtcars dataset to get a set of rankings of car
manufacturer by country of origin. The n column represents the number of
cars a manufacturer has within this dataset and we can use that column as a
way to size the text. We do that in the tab_style() call; the
from_column() function is used within the cell_text() statement to
fashion different font sizes from that n column. This is done in
conjunction with the fn argument of from_column(), which helps to tweak
the values in n to get a useful range of font sizes.
gtcars |>
dplyr::count(mfr, ctry_origin) |>
dplyr::arrange(ctry_origin) |>
gt(groupname_col = "ctry_origin") |>
tab_style(
style = cell_text(
size = from_column(
column = "n",
fn = function(x) paste0(5 + (x * 3), "px")
)
),
locations = cells_body()
) |>
tab_style(
style = cell_text(align = "center"),
locations = cells_row_groups()
) |>
cols_hide(columns = n) |>
tab_options(column_labels.hidden = TRUE) |>
opt_all_caps() |>
opt_vertical_padding(scale = 0.25) |>
cols_align(align = "center", columns = mfr)

Function ID
8-5
Function Introduced
v0.10.0 (October 7, 2023)
See Also
Other helper functions:
adjust_luminance(),
cell_borders(),
cell_fill(),
cell_text(),
currency(),
default_fonts(),
escape_latex(),
google_font(),
gt_latex_dependencies(),
html(),
md(),
nanoplot_options(),
pct(),
px(),
random_id(),
row_group(),
stub(),
system_fonts(),
unit_conversion()
rstudio/gt documentation built on March 29, 2025, 4:02 a.m.
| from_column | R Documentation |
Reference a column of values for certain parameters
Description
It can be useful to obtain parameter values from a column in a
gt for functions that operate on the table body and stub cells. For
example, you might want to indent row labels in the stub. You could call
tab_stub_indent() and indent different rows to various indentation levels.
However, each level of indentation applied necessitates a new call of that
function. To make this better, we can use indentation values available in a
table column via the from_column() helper function. For the
tab_stub_indent() case, you'd invoke this helper at the indent argument
and specify the column that has the values.
Usage
from_column(column, na_value = NULL, fn = NULL)
Arguments
column |
Column name
A single column name in quotation marks. Values will be extracted from this column and provided to compatible arguments. |
na_value |
Default replacement for
A single value to replace any |
fn |
Function to apply
If a function is provided here, any values extracted from the table
|
Value
A list object of class gt_column.
Functions that allow the use of the from_column() helper
Only certain functions (and furthermore a subset of arguments within each)
support the use of from_column() for accessing varying parameter values.
These functions are:
-
tab_stub_indent() -
fmt_number() -
fmt_integer() -
fmt_scientific() -
fmt_engineering() -
fmt_percent() -
fmt_partsper() -
fmt_fraction() -
fmt_currency() -
fmt_roman() -
fmt_index() -
fmt_spelled_num() -
fmt_bytes() -
fmt_date() -
fmt_time() -
fmt_datetime() -
fmt_url() -
fmt_image() -
fmt_flag() -
fmt_markdown() -
fmt_passthrough()
Within help documents for each of these functions you'll find the
Compatibility of arguments with the from_column() helper function section
and sections like these describe which arguments support the use of
from_column().
Examples
from_column() can be used in a variety of formatting functions so that
values for common options don't have to be static, they can change in every
row (so long as you have a column of compatible option values). Here's an
example where we have a table of repeating numeric values along with a column
of currency codes. We can format the numbers to currencies with
fmt_currency() and use from_column() to reference the column of currency
codes, giving us values that are each formatted as having a different
currency.
dplyr::tibble(
amount = rep(30.75, 6),
curr = c("USD", "EUR", "GBP", "CAD", "AUD", "JPY"),
) |>
gt() |>
fmt_currency(currency = from_column(column = "curr"))

Let's summarize the gtcars dataset to get a set of rankings of car
manufacturer by country of origin. The n column represents the number of
cars a manufacturer has within this dataset and we can use that column as a
way to size the text. We do that in the tab_style() call; the
from_column() function is used within the cell_text() statement to
fashion different font sizes from that n column. This is done in
conjunction with the fn argument of from_column(), which helps to tweak
the values in n to get a useful range of font sizes.
gtcars |>
dplyr::count(mfr, ctry_origin) |>
dplyr::arrange(ctry_origin) |>
gt(groupname_col = "ctry_origin") |>
tab_style(
style = cell_text(
size = from_column(
column = "n",
fn = function(x) paste0(5 + (x * 3), "px")
)
),
locations = cells_body()
) |>
tab_style(
style = cell_text(align = "center"),
locations = cells_row_groups()
) |>
cols_hide(columns = n) |>
tab_options(column_labels.hidden = TRUE) |>
opt_all_caps() |>
opt_vertical_padding(scale = 0.25) |>
cols_align(align = "center", columns = mfr)

Function ID
8-5
Function Introduced
v0.10.0 (October 7, 2023)
See Also
Other helper functions:
adjust_luminance(),
cell_borders(),
cell_fill(),
cell_text(),
currency(),
default_fonts(),
escape_latex(),
google_font(),
gt_latex_dependencies(),
html(),
md(),
nanoplot_options(),
pct(),
px(),
random_id(),
row_group(),
stub(),
system_fonts(),
unit_conversion()
Add the following code to your website.
For more information on customizing the embed code, read Embedding Snippets.
