fmt_number_si: Format numbers with SI prefixes
In gt: Easily Create Presentation-Ready Display Tables
fmt_number_si R Documentation
Format numbers with SI prefixes
Description
Format numeric values with SI (International System of Units) prefixes,
automatically selecting the appropriate prefix to keep the mantissa in a
readable range. SI prefixes range from quetta (Q, 10^30) to quecto
(q, 10^-30) and are commonly used in scientific and engineering contexts to
represent very large or very small quantities with units (e.g., "5.2 kW",
"3.8 ng", "1.2 GHz", etc.).
This function provides fine control over SI prefix formatting with the
following options:
unit specification: define a fixed unit or use per-row units from a column
prefix selection: choose between all SI prefixes or only engineering
prefixes (powers of 1000)
precision control: specify decimal places or significant figures
spacing: customize the separator between number, prefix, and unit
locale-based formatting: use locale-specific decimal and thousands separators
Usage
fmt_number_si(
data,
columns = everything(),
rows = everything(),
unit = NULL,
prefix_mode = c("engineering", "decimal"),
decimals = 2,
n_sigfig = NULL,
drop_trailing_zeros = FALSE,
drop_trailing_dec_mark = TRUE,
use_seps = TRUE,
scale_by = 1,
pattern = "{x}",
sep_mark = ",",
dec_mark = ".",
force_sign = FALSE,
incl_space = TRUE,
locale = NULL
)
Arguments
data
The gt table data object
obj:<gt_tbl> // required
This is the gt table object that is commonly created through use of the
gt() function.
columns
Columns to target
<column-targeting expression> // default: everything()
Can either be a series of column names provided in c(), a vector of
column indices, or a select helper function (e.g. starts_with(),
ends_with(), contains(), matches(), num_range() and everything()).
rows
Rows to target
<row-targeting expression> // default: everything()
In conjunction with columns, we can specify which of their rows should
undergo formatting. The default everything() results in all rows in
columns being formatted. Alternatively, we can supply a vector of row
captions within c(), a vector of row indices, or a select helper
function (e.g. starts_with(), ends_with(), contains(), matches(),
num_range(), and everything()). We can also use expressions to filter
down to the rows we need (e.g., [colname_1] > 100 & [colname_2] < 50).
unit
Unit to append to formatted values
scalar<character> // default: NULL (optional)
A character string specifying the unit to append after the SI prefix
(e.g., "g" for grams, "W" for watts, "Hz" for hertz, "m" for meters).
If NULL, only the prefix will be shown. The unit can also be dynamically
specified per row using from_column().
prefix_mode
Type of SI prefixes to use
singl-kw:[engineering|decimal] // default: "engineering"
The type of SI prefixes to use. Options are "engineering" (powers of
1000 only) or "decimal" (all SI prefixes including powers of 10 and 100).
See the SI Prefix Modes section for details.
decimals
Number of decimal places
scalar<numeric|integer>(val>=0) // default: 2
The exact number of decimal places to display in the mantissa. If both
decimals and n_sigfig are provided, n_sigfig takes precedence.
n_sigfig
Number of significant figures
scalar<numeric|integer>(val>=1) // default: NULL (optional)
Format numbers to n significant figures. This is often preferred in
scientific contexts to maintain consistent precision across different
magnitudes. When specified, the decimals argument is ignored.
drop_trailing_zeros
Drop trailing zeros
scalar<logical> // default: FALSE
Remove trailing zeros after the decimal point (e.g., "1.50" becomes "1.5").
drop_trailing_dec_mark
Drop trailing decimal mark
scalar<logical> // default: TRUE
Remove the decimal mark if all decimal places are zero (e.g., "1." becomes
"1").
use_seps
Use digit group separators
scalar<logical> // default: TRUE
Enable or disable the use of digit separators (e.g., thousands separators).
scale_by
Scale values by a fixed multiplier
scalar<numeric|integer> // default: 1
All numeric values will be multiplied by the scale_by value before
undergoing formatting. Since the default value is 1, no values will be
changed unless a different multiplier value is supplied. This is useful
for unit conversions, such as using unit_conversion() to convert
horsepower to watts before formatting with SI prefixes.
pattern
Decoration pattern
scalar<character> // default: "{x}"
A formatting pattern for decorating values. Use {x} to represent the
formatted value (including prefix and unit).
sep_mark
Thousands separator
scalar<character> // default: ","
The character to use as the thousands separator. Overridden if locale is
provided.
dec_mark
Decimal mark
scalar<character> // default: "."
The character to use as the decimal point. Overridden if locale is
provided.
force_sign
Force positive sign
scalar<logical> // default: FALSE
Force the display of a plus sign for positive values.
incl_space
Include a space between the value and the unit symbol
scalar<logical> // default: TRUE
An option for whether to include a space between the numerical value and
the SI prefix + unit (e.g., TRUE for "1.5 kW", FALSE for "1.5kW"). Per
SI convention, there should be a space between the value and the unit
symbol.
locale
Locale identifier
scalar<character> // default: NULL (optional)
An optional locale identifier for locale-specific number formatting.
When provided, overrides sep_mark and dec_mark with locale-appropriate
values.
Value
An object of class gt_tbl.
SI Prefix Modes
The prefix_mode argument controls which SI prefixes are used:
-
"engineering": Uses only prefixes for powers of 1000. This includes:
greater than 1: k (kilo), M (mega), G (giga), T (tera), P (peta),
E (exa), Z (zetta), Y (yotta), R (ronna), Q (quetta)
less than 1: m (milli), u (micro), n (nano), p (pico), f (femto),
a (atto), z (zepto), y (yocto), r (ronto), q (quecto)
this is the most common convention in scientific and engineering
contexts.
-
"decimal": Uses all SI prefixes including those for powers of 10 and 100:
Additional prefixes for greater-than-1 values: da (deca), h (hecto)
Additional prefixes for less-than-1 values: d (deci), c (centi)
This mode is less commonly used but follows the complete SI standard.
Compatibility of formatting function with data values
fmt_number_si() is compatible with body cells that are of the "numeric"
or "integer" types. Any other types of body cells are ignored during
formatting. This is to say that cells of incompatible data types may be
targeted, but there will be no attempt to format them.
Compatibility of arguments with the from_column() helper function
from_column() can be used with certain arguments of fmt_number_si() to
obtain varying parameter values from a specified column within the table.
This means that each row could be formatted a little bit differently. These
arguments provide support for from_column():
-
unit: The unit can be specified with a column name in quotes.
-
decimals: Each row's number formatting could use a different number of
decimal places.
-
n_sigfig: Each row could have a different number of significant figures.
-
drop_trailing_zeros: The option to drop trailing zeros can be controlled
per row.
-
drop_trailing_dec_mark: The option to drop trailing decimal marks can be
controlled per row.
-
use_seps: The use of digit separators can be enabled or disabled on a
per-row basis.
-
scale_by: The scale multiplier can be different for each row.
-
pattern: The formatting pattern can be specified per row.
-
sep_mark: The thousands separator mark can be set per row.
-
dec_mark: The decimal mark can be set per row.
-
force_sign: Whether to force a plus sign can be controlled per row.
-
incl_space: Whether to include a space between number and unit can vary
per row.
-
locale: The locale can be specified per row.
Please note that for all of the aforementioned arguments, a from_column()
call needs to reference a column that has data of the correct type (this is
different for each argument). Additional columns for parameter values can be
generated with cols_add() (if not already present). Columns that contain
parameter data can also be hidden from final display with cols_hide().
Finally, there is no limitation to how many arguments the from_column()
helper is applied so long as the arguments belong to this closed set.
Adapting output to a specific locale
This formatting function can adapt outputs according to a provided locale
value. Examples include "en" for English (United States) and "fr" for
French (France). The use of a valid locale ID here means separator and
decimal marks will be correct for the given locale. Should any values be
provided in sep_mark or dec_mark, they will be overridden by the locale's
preferred values.
Note that a locale value provided here will override any global locale
setting performed in gt()'s own locale argument (it is settable there as
a value received by all other functions that have a locale argument). As a
useful reference on which locales are supported, we can call info_locales()
to view an info table.
Examples
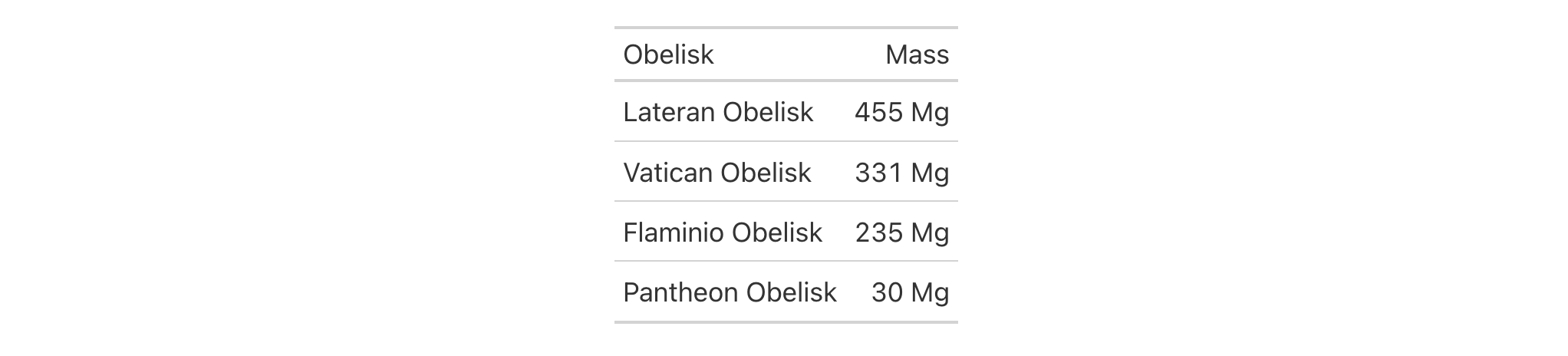
Create a table showing the masses of obelisks located in Rome. The masses are
initially in metric tons, which we'll convert to grams using
unit_conversion() in the scale_by argument. The resulting values are
then formatted with SI prefixes, which are all here as M (mega).
dplyr::tibble(
obelisk = c(
"Lateran Obelisk",
"Vatican Obelisk",
"Flaminio Obelisk",
"Pantheon Obelisk"
),
mass_ton = c(455, 331, 235, 30)
) |>
gt() |>
fmt_number_si(
columns = mass_ton,
unit = "g",
decimals = 0,
scale_by = unit_conversion(
from = "mass.metric-ton",
to = "mass.gram"
)
) |>
cols_label(
obelisk = "Obelisk",
mass_ton = "Mass"
)
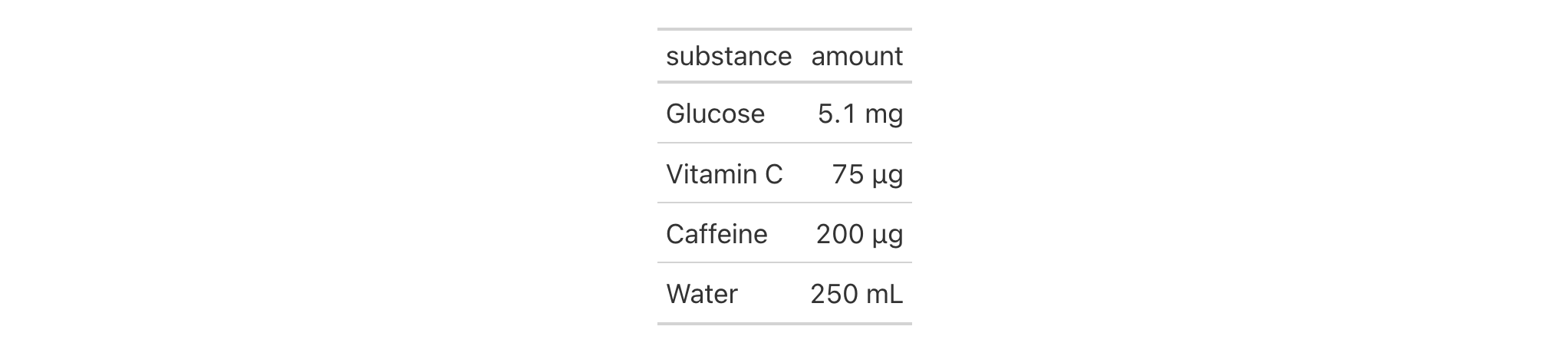
Create a table showing measurements of different substances with varying
units. The unit column contains different units per row (grams and liters),
which are used with from_column() to apply appropriate SI prefixes.
dplyr::tibble(
substance = c("Glucose", "Vitamin C", "Caffeine", "Water"),
amount = c(0.0051, 0.000075, 0.0002, 0.250),
unit = c("g", "g", "g", "L")
) |>
gt() |>
fmt_number_si(
columns = amount,
unit = from_column("unit"),
n_sigfig = 2
) |>
cols_hide(columns = unit)
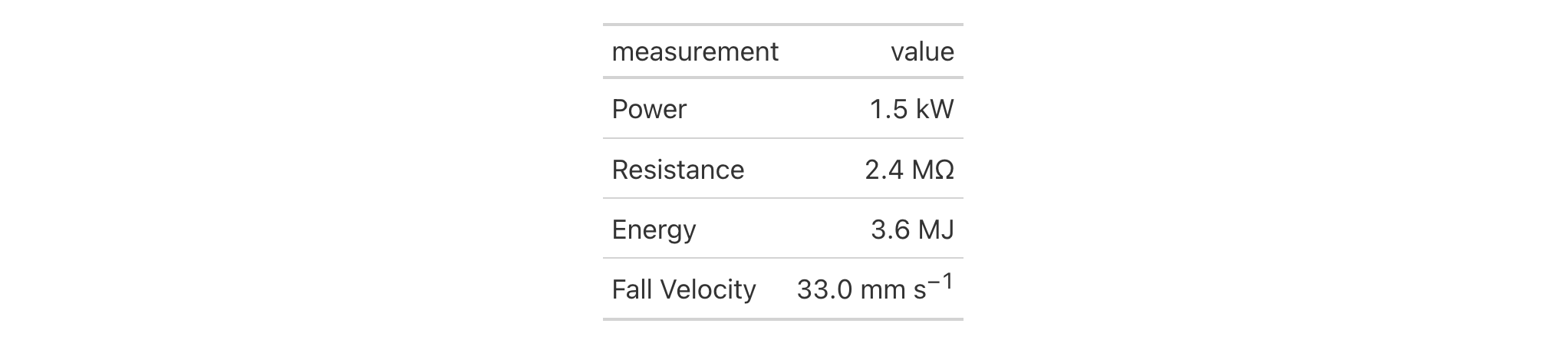
You can combine fmt_number_si() with fmt_units() and cols_merge() to
format measurements with SI prefixes on units that need special typesetting.
In this example, fmt_number_si() handles both the SI prefix and the unit
with proper spacing, while fmt_units() creates a separate column with
additional unit information (like "per hour") that gets merged in.
dplyr::tibble(
measurement = c("Power", "Resistance", "Energy", "Fall Velocity"),
value = c(1500, 2400000, 3600000,0.033),
unit = c("W", ":ohm:", "J", "m /s")
) |>
gt() |>
fmt_number_si(columns = value, decimals = 1) |>
fmt_units(columns = unit) |>
cols_merge(columns = c(value, unit), pattern = "{1}{2}")
Function ID
3-5
Function Introduced
v1.2.0 (December 16, 2025)
See Also
The vector-formatting version of this function:
vec_fmt_number_si().
Other data formatting functions:
data_color(),
fmt(),
fmt_auto(),
fmt_bins(),
fmt_bytes(),
fmt_chem(),
fmt_country(),
fmt_currency(),
fmt_date(),
fmt_datetime(),
fmt_duration(),
fmt_email(),
fmt_engineering(),
fmt_flag(),
fmt_fraction(),
fmt_icon(),
fmt_image(),
fmt_index(),
fmt_integer(),
fmt_markdown(),
fmt_number(),
fmt_partsper(),
fmt_passthrough(),
fmt_percent(),
fmt_roman(),
fmt_scientific(),
fmt_spelled_num(),
fmt_tf(),
fmt_time(),
fmt_units(),
fmt_url(),
sub_large_vals(),
sub_missing(),
sub_small_vals(),
sub_values(),
sub_zero()
gt documentation built on Jan. 22, 2026, 9:07 a.m.
| fmt_number_si | R Documentation |
Format numbers with SI prefixes
Description
Format numeric values with SI (International System of Units) prefixes, automatically selecting the appropriate prefix to keep the mantissa in a readable range. SI prefixes range from quetta (Q, 10^30) to quecto (q, 10^-30) and are commonly used in scientific and engineering contexts to represent very large or very small quantities with units (e.g., "5.2 kW", "3.8 ng", "1.2 GHz", etc.).
This function provides fine control over SI prefix formatting with the following options:
unit specification: define a fixed unit or use per-row units from a column
prefix selection: choose between all SI prefixes or only engineering prefixes (powers of 1000)
precision control: specify decimal places or significant figures
spacing: customize the separator between number, prefix, and unit
locale-based formatting: use locale-specific decimal and thousands separators
Usage
fmt_number_si(
data,
columns = everything(),
rows = everything(),
unit = NULL,
prefix_mode = c("engineering", "decimal"),
decimals = 2,
n_sigfig = NULL,
drop_trailing_zeros = FALSE,
drop_trailing_dec_mark = TRUE,
use_seps = TRUE,
scale_by = 1,
pattern = "{x}",
sep_mark = ",",
dec_mark = ".",
force_sign = FALSE,
incl_space = TRUE,
locale = NULL
)
Arguments
data |
The gt table data object
This is the gt table object that is commonly created through use of the
|
columns |
Columns to target
Can either be a series of column names provided in |
rows |
Rows to target
In conjunction with |
unit |
Unit to append to formatted values
A character string specifying the unit to append after the SI prefix
(e.g., |
prefix_mode |
Type of SI prefixes to use
The type of SI prefixes to use. Options are |
decimals |
Number of decimal places
The exact number of decimal places to display in the mantissa. If both
|
n_sigfig |
Number of significant figures
Format numbers to n significant figures. This is often preferred in
scientific contexts to maintain consistent precision across different
magnitudes. When specified, the |
drop_trailing_zeros |
Drop trailing zeros
Remove trailing zeros after the decimal point (e.g., "1.50" becomes "1.5"). |
drop_trailing_dec_mark |
Drop trailing decimal mark
Remove the decimal mark if all decimal places are zero (e.g., "1." becomes "1"). |
use_seps |
Use digit group separators
Enable or disable the use of digit separators (e.g., thousands separators). |
scale_by |
Scale values by a fixed multiplier
All numeric values will be multiplied by the |
pattern |
Decoration pattern
A formatting pattern for decorating values. Use |
sep_mark |
Thousands separator
The character to use as the thousands separator. Overridden if |
dec_mark |
Decimal mark
The character to use as the decimal point. Overridden if |
force_sign |
Force positive sign
Force the display of a plus sign for positive values. |
incl_space |
Include a space between the value and the unit symbol
An option for whether to include a space between the numerical value and
the SI prefix + unit (e.g., |
locale |
Locale identifier
An optional locale identifier for locale-specific number formatting.
When provided, overrides |
Value
An object of class gt_tbl.
SI Prefix Modes
The prefix_mode argument controls which SI prefixes are used:
-
"engineering": Uses only prefixes for powers of 1000. This includes:greater than 1: k (kilo), M (mega), G (giga), T (tera), P (peta), E (exa), Z (zetta), Y (yotta), R (ronna), Q (quetta)
less than 1: m (milli), u (micro), n (nano), p (pico), f (femto), a (atto), z (zepto), y (yocto), r (ronto), q (quecto)
this is the most common convention in scientific and engineering contexts.
-
"decimal": Uses all SI prefixes including those for powers of 10 and 100:Additional prefixes for greater-than-1 values: da (deca), h (hecto)
Additional prefixes for less-than-1 values: d (deci), c (centi)
This mode is less commonly used but follows the complete SI standard.
Compatibility of formatting function with data values
fmt_number_si() is compatible with body cells that are of the "numeric"
or "integer" types. Any other types of body cells are ignored during
formatting. This is to say that cells of incompatible data types may be
targeted, but there will be no attempt to format them.
Compatibility of arguments with the from_column() helper function
from_column() can be used with certain arguments of fmt_number_si() to
obtain varying parameter values from a specified column within the table.
This means that each row could be formatted a little bit differently. These
arguments provide support for from_column():
-
unit: The unit can be specified with a column name in quotes. -
decimals: Each row's number formatting could use a different number of decimal places. -
n_sigfig: Each row could have a different number of significant figures. -
drop_trailing_zeros: The option to drop trailing zeros can be controlled per row. -
drop_trailing_dec_mark: The option to drop trailing decimal marks can be controlled per row. -
use_seps: The use of digit separators can be enabled or disabled on a per-row basis. -
scale_by: The scale multiplier can be different for each row. -
pattern: The formatting pattern can be specified per row. -
sep_mark: The thousands separator mark can be set per row. -
dec_mark: The decimal mark can be set per row. -
force_sign: Whether to force a plus sign can be controlled per row. -
incl_space: Whether to include a space between number and unit can vary per row. -
locale: The locale can be specified per row.
Please note that for all of the aforementioned arguments, a from_column()
call needs to reference a column that has data of the correct type (this is
different for each argument). Additional columns for parameter values can be
generated with cols_add() (if not already present). Columns that contain
parameter data can also be hidden from final display with cols_hide().
Finally, there is no limitation to how many arguments the from_column()
helper is applied so long as the arguments belong to this closed set.
Adapting output to a specific locale
This formatting function can adapt outputs according to a provided locale
value. Examples include "en" for English (United States) and "fr" for
French (France). The use of a valid locale ID here means separator and
decimal marks will be correct for the given locale. Should any values be
provided in sep_mark or dec_mark, they will be overridden by the locale's
preferred values.
Note that a locale value provided here will override any global locale
setting performed in gt()'s own locale argument (it is settable there as
a value received by all other functions that have a locale argument). As a
useful reference on which locales are supported, we can call info_locales()
to view an info table.
Examples
Create a table showing the masses of obelisks located in Rome. The masses are
initially in metric tons, which we'll convert to grams using
unit_conversion() in the scale_by argument. The resulting values are
then formatted with SI prefixes, which are all here as M (mega).
dplyr::tibble(
obelisk = c(
"Lateran Obelisk",
"Vatican Obelisk",
"Flaminio Obelisk",
"Pantheon Obelisk"
),
mass_ton = c(455, 331, 235, 30)
) |>
gt() |>
fmt_number_si(
columns = mass_ton,
unit = "g",
decimals = 0,
scale_by = unit_conversion(
from = "mass.metric-ton",
to = "mass.gram"
)
) |>
cols_label(
obelisk = "Obelisk",
mass_ton = "Mass"
)

Create a table showing measurements of different substances with varying
units. The unit column contains different units per row (grams and liters),
which are used with from_column() to apply appropriate SI prefixes.
dplyr::tibble(
substance = c("Glucose", "Vitamin C", "Caffeine", "Water"),
amount = c(0.0051, 0.000075, 0.0002, 0.250),
unit = c("g", "g", "g", "L")
) |>
gt() |>
fmt_number_si(
columns = amount,
unit = from_column("unit"),
n_sigfig = 2
) |>
cols_hide(columns = unit)

You can combine fmt_number_si() with fmt_units() and cols_merge() to
format measurements with SI prefixes on units that need special typesetting.
In this example, fmt_number_si() handles both the SI prefix and the unit
with proper spacing, while fmt_units() creates a separate column with
additional unit information (like "per hour") that gets merged in.
dplyr::tibble(
measurement = c("Power", "Resistance", "Energy", "Fall Velocity"),
value = c(1500, 2400000, 3600000,0.033),
unit = c("W", ":ohm:", "J", "m /s")
) |>
gt() |>
fmt_number_si(columns = value, decimals = 1) |>
fmt_units(columns = unit) |>
cols_merge(columns = c(value, unit), pattern = "{1}{2}")

Function ID
3-5
Function Introduced
v1.2.0 (December 16, 2025)
See Also
The vector-formatting version of this function:
vec_fmt_number_si().
Other data formatting functions:
data_color(),
fmt(),
fmt_auto(),
fmt_bins(),
fmt_bytes(),
fmt_chem(),
fmt_country(),
fmt_currency(),
fmt_date(),
fmt_datetime(),
fmt_duration(),
fmt_email(),
fmt_engineering(),
fmt_flag(),
fmt_fraction(),
fmt_icon(),
fmt_image(),
fmt_index(),
fmt_integer(),
fmt_markdown(),
fmt_number(),
fmt_partsper(),
fmt_passthrough(),
fmt_percent(),
fmt_roman(),
fmt_scientific(),
fmt_spelled_num(),
fmt_tf(),
fmt_time(),
fmt_units(),
fmt_url(),
sub_large_vals(),
sub_missing(),
sub_small_vals(),
sub_values(),
sub_zero()
Add the following code to your website.
For more information on customizing the embed code, read Embedding Snippets.
