summary_columns: Add summary columns using aggregation functions
In gt: Easily Create Presentation-Ready Display Tables
View source: R/summary_columns.R
summary_columns R Documentation
Add summary columns using aggregation functions
Description
The summary_columns() function adds one or more computed columns to a table
by aggregating values across selected columns within each row. This is the
horizontal counterpart to summary_rows(), which aggregates down columns to
create summary rows. Common use cases include calculating row totals, row
averages, or other row-wise statistics.
Summary columns are computed immediately when the function is called and are
added to the table's data as regular columns. This means they can be
referenced in subsequent gt operations like cols_move(), fmt_number(),
tab_style(), or even in other computed columns via cols_add().
You can create a single summary column or multiple columns at once by
providing a list of aggregation functions. The functions can be any R
expression that takes a vector of values and returns a single value (like
sum(), mean(), max(), min(), etc.). Column names and labels can be
auto-generated from function names or explicitly specified.
Usage
summary_columns(
data,
columns = everything(),
fns = NULL,
new_col_names = NULL,
new_col_labels = NULL,
fmt = NULL,
side = c("right", "left"),
missing_text = "---"
)
Arguments
data
The gt table data object
obj:<gt_tbl> // required
This is the gt table object that is commonly created through use of the
gt() function.
columns
Columns to aggregate
<column-targeting expression> // default: everything()
The columns to aggregate across for each row. Can either be a series of
column names provided in c(), a vector of column indices, or a select
helper function (e.g. starts_with(), ends_with(), contains(),
matches(), num_range(), and everything()).
fns
Aggregation Expression(s)
<expression|list of expressions>
One or more functions used for aggregation. For a single summary column,
provide a single function as a formula (e.g., ~ sum(.)), character
string (e.g., "sum"), or bare function (e.g., sum). For multiple
summary columns, provide a list of formulas (e.g.,
list(~ sum(.), ~ mean(.), ~ sd(.))). Base functions like mean, min,
max, median, sd, and sum are supported, along with any
user-defined aggregation functions.
new_col_names
Names for new summary columns
vector<character> // default: NULL
Optional names for the new summary columns. Can provide one name for a
single summary column, or multiple names (must match the length of fns)
when adding multiple columns. These names are used as column identifiers
for targeting in other gt functions (e.g., fmt_number(),
tab_style()). If NULL, names will be generated from the function
expressions (e.g., "sum", "mean") or default to "summary_1",
"summary_2", etc.
new_col_labels
Labels for new summary columns
list|vector<character> // default: NULL
Optional labels for the new summary column headers. Can provide one label
for a single column, or multiple labels (must match the length of fns)
when adding multiple columns. Can include plain text or use md() or
html() helpers. If NULL, will use new_col_names as labels.
Important: Use list() instead of c() when mixing plain text with
md() or html() objects to preserve their classes (e.g.,
list("Total", md("**Average**"))).
fmt
Formatting expression
<expression>
An optional formatting expression in formula form. The RHS of ~ should
contain a formatting call (e.g., ~ fmt_number(., decimals = 2)).
side
Side used for placement of summary column
singl-kw:[right|left] // default: "right"
Should the summary column be placed on the "right" (the default) or the
"left" side of the table?
missing_text
Replacement text for NA values
scalar<character> // default: "---"
The text to be used in place of NA values in the summary column cells.
Value
An object of class gt_tbl.
Examples
Use a subset of the countrypops dataset to create a gt table. Add a
summary column that computes the average annual change using
summary_columns().
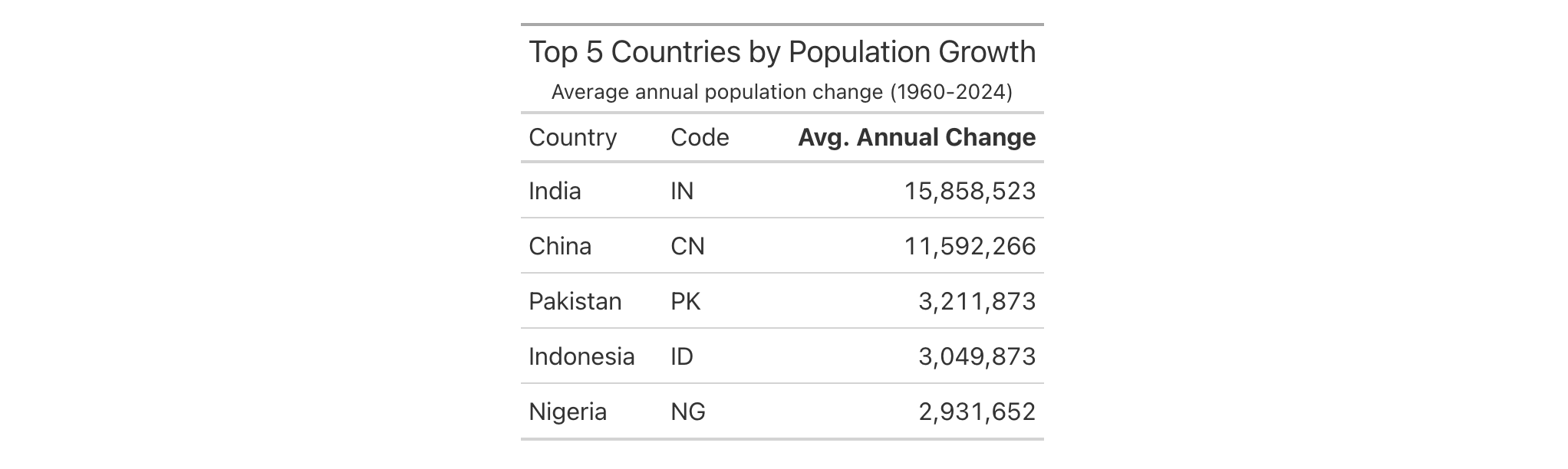
countrypops |>
arrange(country_name, year) |>
group_by(country_name, country_code_2) |>
summarize(
pop_1960 = first(population),
pop_2024 = last(population),
years = n(),
.groups = "drop"
) |>
filter(!is.na(pop_1960), !is.na(pop_2024)) |>
mutate(total_change = pop_2024 - pop_1960) |>
slice_max(total_change, n = 5) |>
select(country_name, country_code_2, pop_1960, pop_2024, years) |>
gt() |>
summary_columns(
columns = c(pop_1960, pop_2024, years),
fns = ~ (.[2] - .[1]) / (.[3] - 1),
new_col_names = "avg_annual_change",
new_col_labels = md("**Avg. Annual Change**") # No list() needed!
) |>
cols_hide(columns = c(pop_1960, pop_2024, years)) |>
fmt_integer() |>
cols_label(
country_name = "Country",
country_code_2 = "Code"
) |>
tab_header(
title = "Top 5 Countries by Population Growth",
subtitle = "Average annual population change (1960-2024)"
)
Function ID
6-6
Function Introduced
v1.2.0 (December 16, 2025)
See Also
Other row addition/modification functions:
grand_summary_rows(),
row_group_order(),
row_order(),
rows_add(),
summary_rows()
gt documentation built on Jan. 22, 2026, 9:07 a.m.
View source: R/summary_columns.R
| summary_columns | R Documentation |
Add summary columns using aggregation functions
Description
The summary_columns() function adds one or more computed columns to a table
by aggregating values across selected columns within each row. This is the
horizontal counterpart to summary_rows(), which aggregates down columns to
create summary rows. Common use cases include calculating row totals, row
averages, or other row-wise statistics.
Summary columns are computed immediately when the function is called and are
added to the table's data as regular columns. This means they can be
referenced in subsequent gt operations like cols_move(), fmt_number(),
tab_style(), or even in other computed columns via cols_add().
You can create a single summary column or multiple columns at once by
providing a list of aggregation functions. The functions can be any R
expression that takes a vector of values and returns a single value (like
sum(), mean(), max(), min(), etc.). Column names and labels can be
auto-generated from function names or explicitly specified.
Usage
summary_columns(
data,
columns = everything(),
fns = NULL,
new_col_names = NULL,
new_col_labels = NULL,
fmt = NULL,
side = c("right", "left"),
missing_text = "---"
)
Arguments
data |
The gt table data object
This is the gt table object that is commonly created through use of the
|
columns |
Columns to aggregate
The columns to aggregate across for each row. Can either be a series of
column names provided in |
fns |
Aggregation Expression(s)
One or more functions used for aggregation. For a single summary column,
provide a single function as a formula (e.g., |
new_col_names |
Names for new summary columns
Optional names for the new summary columns. Can provide one name for a
single summary column, or multiple names (must match the length of |
new_col_labels |
Labels for new summary columns
Optional labels for the new summary column headers. Can provide one label
for a single column, or multiple labels (must match the length of |
fmt |
Formatting expression
An optional formatting expression in formula form. The RHS of |
side |
Side used for placement of summary column
Should the summary column be placed on the |
missing_text |
Replacement text for
The text to be used in place of |
Value
An object of class gt_tbl.
Examples
Use a subset of the countrypops dataset to create a gt table. Add a
summary column that computes the average annual change using
summary_columns().
countrypops |>
arrange(country_name, year) |>
group_by(country_name, country_code_2) |>
summarize(
pop_1960 = first(population),
pop_2024 = last(population),
years = n(),
.groups = "drop"
) |>
filter(!is.na(pop_1960), !is.na(pop_2024)) |>
mutate(total_change = pop_2024 - pop_1960) |>
slice_max(total_change, n = 5) |>
select(country_name, country_code_2, pop_1960, pop_2024, years) |>
gt() |>
summary_columns(
columns = c(pop_1960, pop_2024, years),
fns = ~ (.[2] - .[1]) / (.[3] - 1),
new_col_names = "avg_annual_change",
new_col_labels = md("**Avg. Annual Change**") # No list() needed!
) |>
cols_hide(columns = c(pop_1960, pop_2024, years)) |>
fmt_integer() |>
cols_label(
country_name = "Country",
country_code_2 = "Code"
) |>
tab_header(
title = "Top 5 Countries by Population Growth",
subtitle = "Average annual population change (1960-2024)"
)

Function ID
6-6
Function Introduced
v1.2.0 (December 16, 2025)
See Also
Other row addition/modification functions:
grand_summary_rows(),
row_group_order(),
row_order(),
rows_add(),
summary_rows()
Add the following code to your website.
For more information on customizing the embed code, read Embedding Snippets.
