tab_header: Add a table header
In rstudio/gt: Easily Create Presentation-Ready Display Tables
View source: R/tab_create_modify.R
tab_header R Documentation
Add a table header
Description
We can add a table header to the gt table with a title and even a
subtitle using tab_header(). A table header is an optional
table part that is positioned just above the column labels table part. We
have the flexibility to use Markdown or HTML formatting for the header's
title and subtitle with the md() and html() helper functions.
Usage
tab_header(data, title, subtitle = NULL, preheader = NULL)
Arguments
data
The gt table data object
obj:<gt_tbl> // required
This is the gt table object that is commonly created through use of the
gt() function.
title
Header title
scalar<character> // required
Text to be used in the table title. We can elect to use the md() and
html() helper functions to style the text as Markdown or to retain HTML
elements in the text.
subtitle
Header subtitle
scalar<character> // default: NULL (optional)
Text to be used in the table subtitle. We can elect to use md() or
html() helper functions to style the text as Markdown or to retain HTML
elements in the text.
preheader
RTF preheader text
vector<character> // default: NULL (optional)
Optional preheader content that is rendered above the table for RTF output.
Can be supplied as a vector of text.
Value
An object of class gt_tbl.
Examples
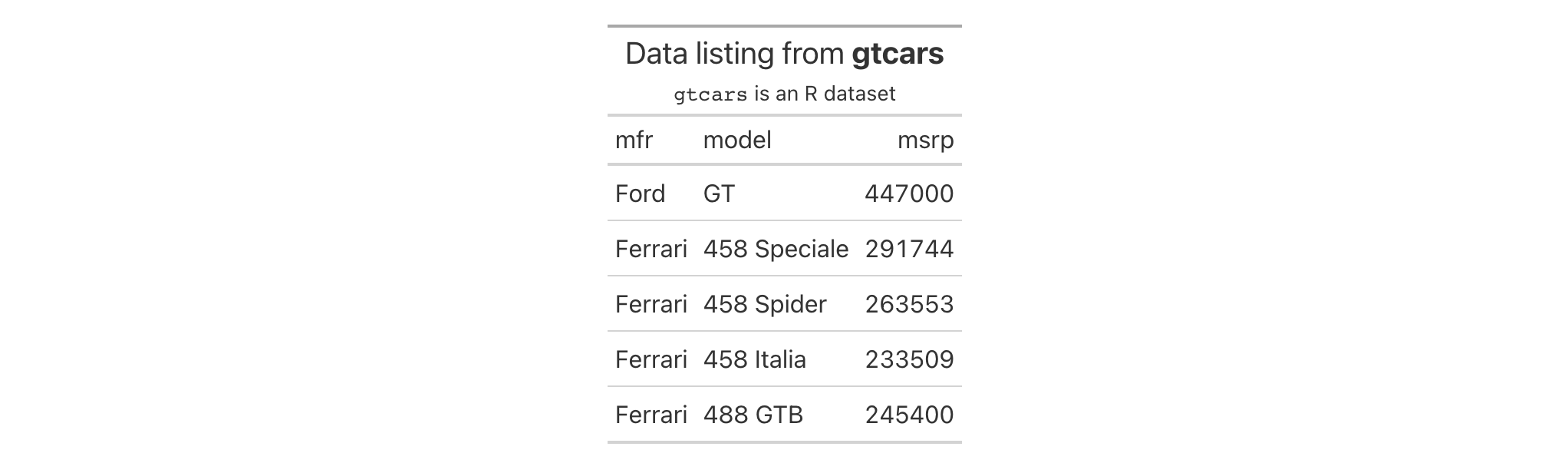
Let's use a small portion of the gtcars dataset to create a gt table.
A header part can be added to the table with the tab_header() function.
We'll add a title and the optional subtitle as well. With md(), we can
make sure the Markdown formatting is interpreted and transformed.
gtcars |>
dplyr::select(mfr, model, msrp) |>
dplyr::slice(1:5) |>
gt() |>
tab_header(
title = md("Data listing from **gtcars**"),
subtitle = md("`gtcars` is an R dataset")
)
If the table is intended solely as an HTML table, you could introduce your
own HTML elements into the header. You can even use the htmltools package
to help arrange and generate the HTML. Here's an example of that, where two
<div> elements are placed in a htmltools::tagList().
gtcars |>
dplyr::select(mfr, model, msrp) |>
dplyr::slice(1:5) |>
gt() |>
tab_header(
title =
htmltools::tagList(
htmltools::tags$div(
htmltools::HTML(
web_image("https://www.r-project.org/logo/Rlogo.png")
),
style = htmltools::css(`text-align` = "center")
),
htmltools::tags$div(
"Data listing from ", htmltools::tags$strong("gtcars")
)
)
)

If using HTML but doing something far simpler, we can wrap our title or
subtitle inside html() to declare that the text provided is HTML.
gtcars |>
dplyr::select(mfr, model, msrp) |>
dplyr::slice(1:5) |>
gt() |>
tab_header(
title = html("Data listing from <strong>gtcars</strong>"),
subtitle = html("From <span style='color:red;'>gtcars</span>")
)

Sometimes, aligning the heading elements to the left can improve the
presentation of a table. Here, we use the nuclides dataset to generate a
display of natural abundance values for several stable isotopes.
opt_align_table_header() is used with align = "left" to make it so the
title and subtitle are left aligned in the header area.
nuclides |>
dplyr::filter(!is.na(abundance)) |>
dplyr::filter(abundance != 1) |>
dplyr::filter(z >= 1 & z <= 8) |>
dplyr::mutate(element = paste0(element, ", **z = ", z, "**")) |>
dplyr::mutate(nuclide = gsub("[0-9]+$", "", nuclide)) |>
dplyr::select(nuclide, element, atomic_mass, abundance, abundance_uncert) |>
gt(
rowname_col = "nuclide",
groupname_col = "element",
process_md = TRUE
) |>
tab_header(
title = "Natural Abundance Values",
subtitle = md("For elements having atomic numbers from `1` to `8`.")
) |>
tab_stubhead(label = "Isotope") |>
tab_stub_indent(
rows = everything(),
indent = 1
) |>
fmt_chem(columns = stub()) |>
fmt_number(
columns = atomic_mass,
decimals = 4,
scale_by = 1 / 1e6
) |>
fmt_percent(
columns = contains("abundance"),
decimals = 4
) |>
cols_merge_uncert(
col_val = abundance,
col_uncert = abundance_uncert
) |>
cols_label_with(fn = function(x) tools::toTitleCase(gsub("_", " ", x))) |>
cols_width(
stub() ~ px(70),
atomic_mass ~ px(120),
abundance ~ px(200)
) |>
opt_align_table_header(align = "left") |>
opt_vertical_padding(scale = 0.5)

Function ID
2-1
Function Introduced
v0.2.0.5 (March 31, 2020)
See Also
Other part creation/modification functions:
tab_caption(),
tab_footnote(),
tab_info(),
tab_options(),
tab_row_group(),
tab_source_note(),
tab_spanner(),
tab_spanner_delim(),
tab_stub_indent(),
tab_stubhead(),
tab_style(),
tab_style_body()
rstudio/gt documentation built on March 29, 2025, 4:02 a.m.
View source: R/tab_create_modify.R
| tab_header | R Documentation |
Add a table header
Description
We can add a table header to the gt table with a title and even a
subtitle using tab_header(). A table header is an optional
table part that is positioned just above the column labels table part. We
have the flexibility to use Markdown or HTML formatting for the header's
title and subtitle with the md() and html() helper functions.
Usage
tab_header(data, title, subtitle = NULL, preheader = NULL)
Arguments
data |
The gt table data object
This is the gt table object that is commonly created through use of the
|
title |
Header title
Text to be used in the table title. We can elect to use the |
subtitle |
Header subtitle
Text to be used in the table subtitle. We can elect to use |
preheader |
RTF preheader text
Optional preheader content that is rendered above the table for RTF output. Can be supplied as a vector of text. |
Value
An object of class gt_tbl.
Examples
Let's use a small portion of the gtcars dataset to create a gt table.
A header part can be added to the table with the tab_header() function.
We'll add a title and the optional subtitle as well. With md(), we can
make sure the Markdown formatting is interpreted and transformed.
gtcars |>
dplyr::select(mfr, model, msrp) |>
dplyr::slice(1:5) |>
gt() |>
tab_header(
title = md("Data listing from **gtcars**"),
subtitle = md("`gtcars` is an R dataset")
)

If the table is intended solely as an HTML table, you could introduce your
own HTML elements into the header. You can even use the htmltools package
to help arrange and generate the HTML. Here's an example of that, where two
<div> elements are placed in a htmltools::tagList().
gtcars |>
dplyr::select(mfr, model, msrp) |>
dplyr::slice(1:5) |>
gt() |>
tab_header(
title =
htmltools::tagList(
htmltools::tags$div(
htmltools::HTML(
web_image("https://www.r-project.org/logo/Rlogo.png")
),
style = htmltools::css(`text-align` = "center")
),
htmltools::tags$div(
"Data listing from ", htmltools::tags$strong("gtcars")
)
)
)

If using HTML but doing something far simpler, we can wrap our title or
subtitle inside html() to declare that the text provided is HTML.
gtcars |>
dplyr::select(mfr, model, msrp) |>
dplyr::slice(1:5) |>
gt() |>
tab_header(
title = html("Data listing from <strong>gtcars</strong>"),
subtitle = html("From <span style='color:red;'>gtcars</span>")
)

Sometimes, aligning the heading elements to the left can improve the
presentation of a table. Here, we use the nuclides dataset to generate a
display of natural abundance values for several stable isotopes.
opt_align_table_header() is used with align = "left" to make it so the
title and subtitle are left aligned in the header area.
nuclides |>
dplyr::filter(!is.na(abundance)) |>
dplyr::filter(abundance != 1) |>
dplyr::filter(z >= 1 & z <= 8) |>
dplyr::mutate(element = paste0(element, ", **z = ", z, "**")) |>
dplyr::mutate(nuclide = gsub("[0-9]+$", "", nuclide)) |>
dplyr::select(nuclide, element, atomic_mass, abundance, abundance_uncert) |>
gt(
rowname_col = "nuclide",
groupname_col = "element",
process_md = TRUE
) |>
tab_header(
title = "Natural Abundance Values",
subtitle = md("For elements having atomic numbers from `1` to `8`.")
) |>
tab_stubhead(label = "Isotope") |>
tab_stub_indent(
rows = everything(),
indent = 1
) |>
fmt_chem(columns = stub()) |>
fmt_number(
columns = atomic_mass,
decimals = 4,
scale_by = 1 / 1e6
) |>
fmt_percent(
columns = contains("abundance"),
decimals = 4
) |>
cols_merge_uncert(
col_val = abundance,
col_uncert = abundance_uncert
) |>
cols_label_with(fn = function(x) tools::toTitleCase(gsub("_", " ", x))) |>
cols_width(
stub() ~ px(70),
atomic_mass ~ px(120),
abundance ~ px(200)
) |>
opt_align_table_header(align = "left") |>
opt_vertical_padding(scale = 0.5)

Function ID
2-1
Function Introduced
v0.2.0.5 (March 31, 2020)
See Also
Other part creation/modification functions:
tab_caption(),
tab_footnote(),
tab_info(),
tab_options(),
tab_row_group(),
tab_source_note(),
tab_spanner(),
tab_spanner_delim(),
tab_stub_indent(),
tab_stubhead(),
tab_style(),
tab_style_body()
Add the following code to your website.
For more information on customizing the embed code, read Embedding Snippets.
